- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Past Issue in 2017
Volume: 7, Issue: 7
Biochemistry
Nitroxide Labeling of Proteins and the Determination of Paramagnetic Relaxation Derived Distance Restraints for NMR Studies
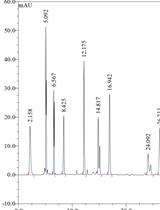
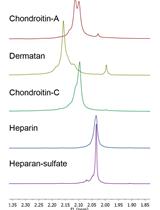
Heparan Sulfate Identification and Characterisation: Method II. Enzymatic Depolymerisation and SAX-HPLC Analysis to Determine Disaccharide Composition
Heparan Sulfate Identification and Characterisation: Method I. Heparan Sulfate Identification by NMR Analysis
Isolation and Analysis of Proteoglycans and Glycosaminoglycans from Archaeological Bones and Teeth
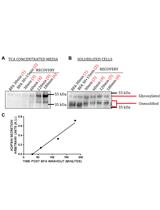
Secretion of Adipsin as an Assay to Measure Flux from the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Cell Biology
Gliding Assay to Analyze Microtubule-based Motor Protein Dynamics
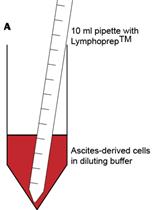
Isolation of Mononuclear Cell Populations from Ovarian Carcinoma Ascites
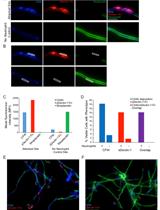
In vivo Live Imaging of Calcium Waves and Other Cellular Processes during Fertilization in Caenorhabditis elegans
In vitro Microtubule Bundling Assay under Physiological Conditions
Developmental Biology
Assessment of Murine Retinal Function by Electroretinography
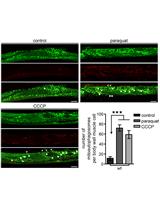
In vivo Mitophagy Monitoring in Caenorhabditis elegans to Determine Mitochondrial Homeostasis
Immunology
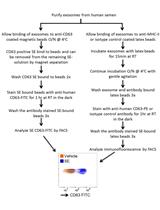
Isolation of Exosomes from Semen for in vitro Uptake and HIV-1 Infection Assays
Screening for Novel Endogenous Inflammatory Stimuli Using the Secreted Embryonic Alkaline Phosphatase NF-κB Reporter Assay
In vitro Detection of Neutrophil Traps and Post-attack Cell Wall Changes in Candida Hyphae
Microbiology
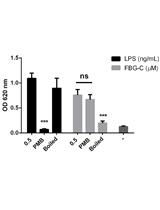
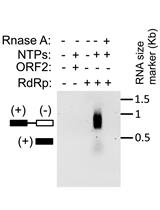
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase Assay for Hepatitis E Virus
Measurement of the Galactanase Activity of the GanB Galactanase Protein from Bacillus subtilis
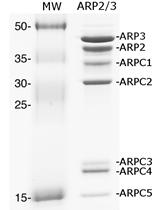
ARP2/3 Phosphorylation Assay in the Presence of Recombinant Bacterial Effectors
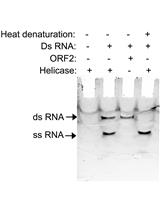
RNA Strand Displacement Assay for Hepatitis E Virus Helicase
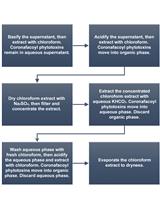
Purification of N-coronafacoyl Phytotoxins from Streptomyces scabies
Molecular Biology
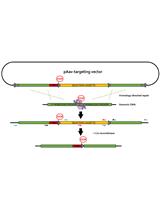
Robust Generation of Knock-in Cell Lines Using CRISPR-Cas9 and rAAV-assisted Repair Template Delivery
Efficient Generation of Multi-gene Knockout Cell Lines and Patient-derived Xenografts Using Multi-colored Lenti-CRISPR-Cas9
Neuroscience
Testing Depression in Mice: a Chronic Social Defeat Stress Model
Measuring Behavioral Individuality in the Acoustic Startle Behavior in Zebrafish
Plant Science
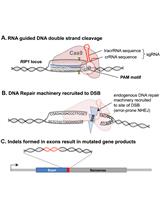
Use of Geminivirus for Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 Components to Tobacco by Agro-infiltration
Analyses of Root-secreted Acid Phosphatase Activity in Arabidopsis
Resin-embedded Thin-section Immunohistochemistry Coupled with Triple Cellular Counterstaining
Stem Cell
A Co-culture Model for Determining the Target Specificity of the de novo Generated Retinal Ganglion Cells