- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Past Issue in 2018
Volume: 8, Issue: 13
Biochemistry
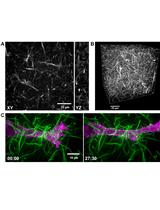
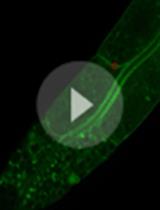
Fluorescent Labeling of Rat-tail Collagen for 3D Fluorescence Imaging
Assessment of Uptake and Biodistribution of Radiolabeled Cholesterol in Mice Using Gavaged Recombinant Triglyceride-rich Lipoprotein Particles (rTRL)
Cancer Biology
An in vitro Co-culture System for the Activation of CD40 by Membrane-presented CD40 Ligand versus Soluble Agonist
Cell Biology
FRAP: A Powerful Method to Evaluate Membrane Fluidity in Caenorhabditis elegans
Developmental Biology
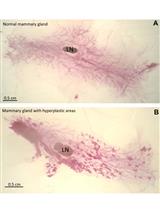
Mouse Mammary Gland Whole Mount Preparation and Analysis
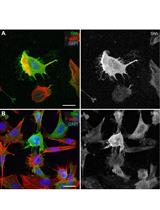
Preserve Cultured Cell Cytonemes through a Modified Electron Microscopy Fixation
Microbiology
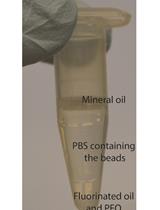
Bacterial Microcolonies in Gel Beads for High-throughput Screening
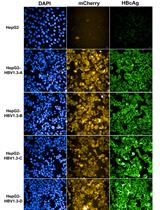
Sleeping Beauty Transposon-based System for Rapid Generation of HBV-replicating Stable Cell Lines
Induction of Natural Competence in Genetically-modified Lactococcus lactis
Neuroscience
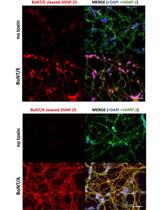
Preparation of Cerebellum Granule Neurons from Mouse or Rat Pups and Evaluation of Clostridial Neurotoxin Activity and Their Inhibitors by Western Blot and Immunohistochemistry
Brain Tissue Culture of Per2::Luciferase Transgenic Mice for ex vivo Bioluminescence
Plant Science
An Optimized CTAB Method for Genomic DNA Extraction from Freshly-picked Pinnae of Fern, Adiantum capillus-veneris L.
Quantification of Starch in Guard Cells of Arabidopsis thaliana
Separation of Thylakoid Protein Complexes with Two-dimensional Native-PAGE
Isolation of Intact Vacuoles from Petunia Petals and Extraction of Sequestered Glycosylated Phenylpropanoid Compounds
A Modified Approach for Axenic Cultivation of Spores of Fern Adiantum capillus-veneris L. with High Germination Rate