- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Past Issue in 2018
Volume: 8, Issue: 14
Biochemistry
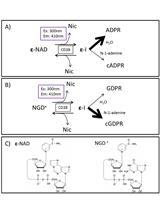
Measuring CD38 Hydrolase and Cyclase Activities: 1,N6-Ethenonicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (ε-NAD) and Nicotinamide Guanine Dinucleotide (NGD) Fluorescence-based Methods
Two Different Methods of Quantification of Oxidized Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) and Reduced Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NADH) Intracellular Levels: Enzymatic Coupled Cycling Assay and Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC)-Mass Spectrometry
In vitro Enzymatic Assays of Histone Decrotonylation on Recombinant Histones
BMV Propagation, Extraction and Purification Using Chromatographic Methods
Cell Biology
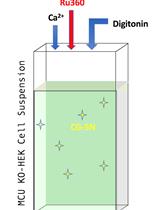
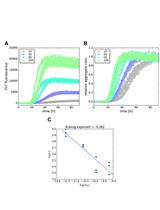
Fluorophore-Based Mitochondrial Ca2+ Uptake Assay
Developmental Biology
Muscle Function Assessment Using a Drosophila Larvae Crawling Assay
Immunology
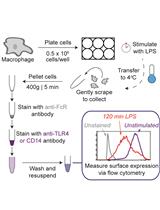
Measurement of TLR4 and CD14 Receptor Endocytosis Using Flow Cytometry
Microbiology
Single and Multiplexed Gene Editing in Ustilago maydis Using CRISPR-Cas9
Molecular Biology
α-Synuclein Aggregation Monitored by Thioflavin T Fluorescence Assay
Neuroscience
Evaluating Working Memory on a T-maze in Male Rats
Ex vivo Whole-cell Recordings in Adult Drosophila Brain
Assessing Experience-dependent Tuning of Song Preference in Fruit Flies (Drosophila melanogaster)
Embryonic Intravitreous Injection in Mouse
Plant Science
High Resolution Melting Temperature Analysis to Identify CRISPR/Cas9 Mutants from Arabidopsis
Extraction of RNA from Recalcitrant Tree Species Paulownia elongata