- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Past Issue in 2015
Volume: 5, Issue: 20
Cancer Biology
Rat Aortic Ring Model to Assay Angiogenesis ex vivo
Cell Biology
In vivo Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-dextran (FD4) Permeability Assay
Intravenous Tomato Lectin Injection to Assess Functional Vasculature
Immunology
Immune Cell Isolation from Mouse Femur Bone Marrow
Isolation and Culture of Human Endometrial Epithelial Cells and Stromal Fibroblasts
Collagen-induced Arthritis: A Model for Murine Autoimmune Arthritis
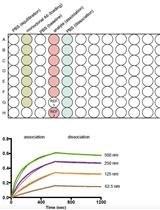
Kinetic Analysis of Monoclonal Antibody Binding to HIV-1 gp120-derived Hyperglycosylated Cores
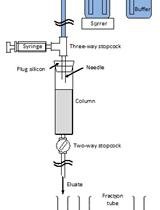
Coupling of HIV-1 gp120-derived Core Protein to Paramagnetic Beads and Adsorption Assays
Microbiology
Product Analysis of Starch Active Enzymes by TLC
Purification of a Protein Exhibiting Isoleucine 2-epimerase Activity from Lactobacillus otakiensis JCM 15040
Plant Science
Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis (Downy Mildew) Infection Assay in Arabidopsis
Isolation of Triterpenes from Propolis (Bee Glue)
Isolation and Characterization Procedure for Indole Alkaloids from the Marquesan Plant Rauvolfia Nukuhivensis
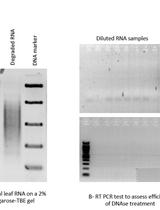
Mitochondrial RNA Transcript Analysis Assay of Arabidopsis Leaf Tissues
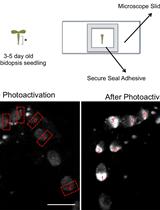
Two-photon Photoactivation to Measure Histone Exchange Dynamics in Plant Root Cells
Vacuole Structure Analysis during Cell Death Subsequent to Application of Erwinia carotovora Culture Filtrates to Cell Cultures of Nicotiana tabacum
Stem Cell
Clonal Culture of Mouse Liver Progenitor Cells