- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Past Issue in 2023
Volume: 13, Issue: 17
Biochemistry
An in vitro Assay to Probe the Formation of Biomolecular Condensates
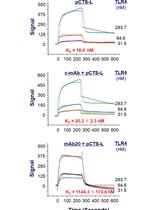
Use of Open Surface Plasmon Resonance (OpenSPR) to Characterize the Binding Affinity of Protein–Protein Interactions
Cell Biology
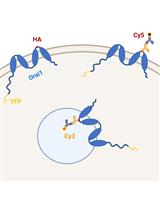
Methods to Quantify the Dynamic Recycling of Plasma Membrane Channels
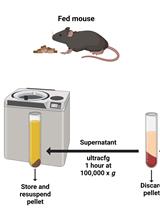
Endoplasmic Reticulum Isolation: An Optimized Approach into Cells and Mouse Liver Fractionation
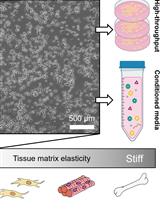
A Large-format Polyacrylamide Gel with Controllable Matrix Mechanics for Mammalian Cell Culture and Conditioned Media Production
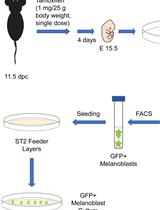
Isolation, Purification, and Culture of Embryonic Melanoblasts from Green Fluorescent Protein–expressing Reporter Mice
Developmental Biology
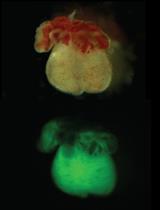
Isolation of Embryonic Cardiomyocytes and Cell Proliferation Assay Using Genetically Engineered Reporter Mouse Model
Immunology
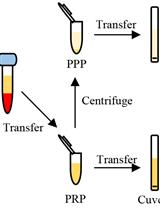
Determination of Antibody Activity by Platelet Aggregation
Microbiology
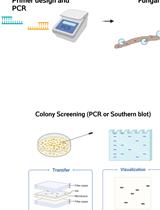
Gene Replacement by a Selectable Marker in the Filamentous Fungus Magnaporthe oryzae
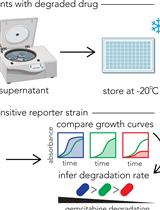
Functional Assay for Measuring Bacterial Degradation of Gemcitabine Chemotherapy
Molecular Biology
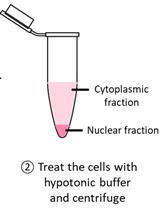
Detection of Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Circular RNA via RT-qPCR
Fast and Sustainable Thermo-osmotic DNA Extraction Protocol for Trans-spectrum Contingency and Field Use
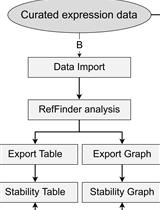
Expression Stability Analysis of Candidate References for Normalization of RT-qPCR Data Using RefSeeker R package
Neuroscience
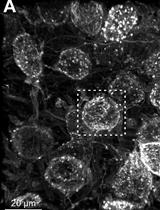
Confocal Imaging and 3D Reconstruction to Determine How Genetic Perturbations Impact Presynaptic Morphology at the Mouse Calyx of Held
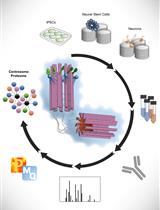
Spatial Centrosome Proteomic Profiling of Human iPSC-derived Neural Cells
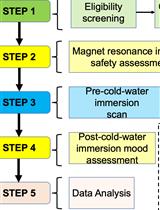
The Effects of Whole-body Cold-water Immersion on Brain Connectivity Related to the Affective State in Adults Using fMRI: A Protocol of a Pre-post Experimental Design
Plant Science
An In-depth Guide to the Ultrastructural Expansion Microscopy (U-ExM) of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
A Protocol for Mitotic Metaphase Chromosome Count Using Shoot Meristematic Tissues of Mulberry Tree Species
An Optimized Protocol for Detecting Guard Cell–specific Gene Expression by in situ RT-PCR in Brassica rapa
13CO2-labelling and Sampling in Algae for Flux Analysis of Photosynthetic and Central Carbon Metabolism
Stem Cell
Absolute Quantification of mRNA Isoforms in Adult Stem Cells Using Microfluidic Digital PCR