- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Past Issue in 2017
Volume: 7, Issue: 1
Biochemistry
Measuring Oxidative Stress in Caenorhabditis elegans: Paraquat and Juglone Sensitivity Assays
Examination of the Interaction between a Membrane Active Peptide and Artificial Bilayers by Dual Polarisation Interferometry
Cancer Biology
In vivo Efficacy Studies in Cell Line and Patient-derived Xenograft Mouse Models
Relative Stiffness Measurements of Cell-embedded Hydrogels by Shear Rheology in vitro
Measuring Procaspase-8 and -10 Processing upon Apoptosis Induction
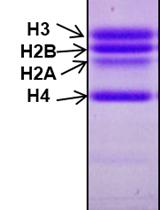
In vitro Histone H3 Cleavage Assay for Yeast and Chicken Liver H3 Protease
Generation of Tumour-stroma Minispheroids for Drug Efficacy Testing
Immunology
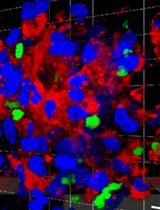
Simultaneous Intranasal/Intravascular Antibody Labeling of CD4+ T Cells in Mouse Lungs
FICZ Exposure and Viral Infection in Mice
In vitro Treatment of Mouse and Human Cells with Endogenous Ligands for Activation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
Microbiology
Bacterial Intracellular Sodium Ion Measurement using CoroNa Green
Measurements of Free-swimming Speed of Motile Salmonella Cells in Liquid Media
Fluorescence in situ Localization of Gene Expression Using a lacZ Reporter in the Heterocyst-forming Cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis
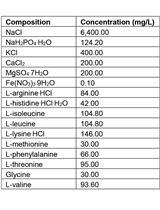
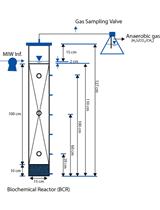
Pilot-scale Columns Equipped with Aqueous and Solid-phase Sampling Ports Enable Geochemical and Molecular Microbial Investigations of Anoxic Biological Processes
Neuroscience
Primary Culture of Mouse Neurons from the Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn
Optogenetic Mapping of Synaptic Connections in Mouse Brain Slices to Define the Functional Connectome of Identified Neuronal Populations
Plant Science
Dot Blot Analysis of N6-methyladenosine RNA Modification Levels
Cation (Ca2+ and Mn2+) Partitioning Assays with Intact Arabidopsis Chloroplasts
In vitro Ubiquitin Dimer Formation Assay
Stem Cell
Ex vivo Culture of Fetal Mouse Gastric Epithelial Progenitors
Ex vivo Culture of Adult Mouse Antral Glands