- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Amino Acid Racemase Enzyme Assays
Published: Vol 4, Iss 9, May 5, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1112 Views: 9041
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
In vitro Nitrate Reductase Activity Assay of Mycolicibacterium smegmatis Crude Extract
Wei Tan [...] Guo-Ping Zhao
Jul 20, 2021 2098 Views
Assay for Protealysin-like Protease Inhibitor Activity
Igor M. Berdyshev [...] Ilya V. Demidyuk
Oct 5, 2022 701 Views
H2 Production from Methyl Viologen–Dependent Hydrogenase Activity Monitored by Gas Chromatography
Nuttavut Kosem
Dec 5, 2023 130 Views
Abstract
Amino acid racemases are enzymes that invert the α-carbon stereochemistry of amino acids (AAs), interconverting amino acids between their L- and D-enantiomers in a reversible reaction. In bacteria, they are known to have catabolic physiological functions but are also involved in the synthesis of many D-AAs, including D-glutamate and D-alanine, which are necessary components of the peptidoglycan layer of the bacterial cell wall. As such, amino acid racemases represent significant targets for the development of bactericidal compounds. Amino acid racemases are also regarded by the biotechnological industry as important catalysts for the production of economically relevant D-AAs. Here, we provide a detailed protocol using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl-5-L-alanine amide (FDAA, also Marfey’s reagent) for the characterization of novel amino acid racemases. The protocol described here was designed to obtain accurate kinetic parameters (kcat, KM values). Enzyme concentrations and reaction times were optimized so as to minimize the reverse reaction, which can confound results when measuring racemase reactions.
Materials and Reagents
- Escherichia coli (E. coli) Rosetta 2 (DE3) cell line
- pET overexpression system
- His-tag and Ni2+-NTA affinity chromatography (HIS-Select Nickel Affinity Gel) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6611 )
- AA substrates
Note: Each enantiomer of the 19 chiral proteinogenic AAs, and the four epimers of hydroxyproline, are prepared in 50 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.4) with any co-factors (PLP at 20 μM was used in our case.). - 0.5% solution (w/v, in acetone) of Marfey’s reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 71478 )
- 1 M NaHCO3
- 2 M HCl
- 2 M NaOH
- HPLC buffer (0.05 M TEAP buffer, pH 3.0) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Bottle top filter (polystyrene) (Corning, catalog number: 430513 ) (filter used in TEAP buffer preparation)
- Syringe filter (PTFE) (Tisch Scientific, catalog number: SF14466 ) (filter used in HPLC sample preparation)
- Heat block (set at 37 °C for enzyme reactions)
- Heat block (set at 40 °C for derivatization of reaction products)
- 2 ml microfuge tubes (for the reaction, derivatization, and dilution of derivatized products)
- Amber HPLC vials with caps, syringes (1 ml), needles, and filtersfilters (0.22 μm polytetrafluoroethylene, PTFE)
- Waters Nova-Pak (C18 column) (3.9 mm by 150 mm)
Software
- Microsoft Excel
Procedure
- Enzyme preparation and storage
- Enzyme was overexpressed using E. coli Rosetta 2 (DE3) cell line and the pET overexpression system, His-tag and Ni2+-NTA affinity chromatography [for specifics, please see Goodlett et al. (1995)].
- After chromatography and buffer exchange, the enzyme was divided into 50 μl aliquots and was snap-frozen before long-term storage at -80 °C.
- Enzyme was overexpressed using E. coli Rosetta 2 (DE3) cell line and the pET overexpression system, His-tag and Ni2+-NTA affinity chromatography [for specifics, please see Goodlett et al. (1995)].
- Enzyme assays
- Enzyme reactions were performed in 2 ml microfuge tubes.
- 199 μl of AA solution in 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) plus cofactors (if needed) were placed in each reaction tube.
- 20 μM pyridoxal-5’-phosphate (PLP) was added based on bioinformatic evidence that the enzyme has a PLP-binding motif.
- To pre-condition the assay solution, the assay tubes were kept at 37 °C for 5 min before enzyme addition.
- Assay was initiated by the addition of the purified enzyme to a final volume of 200 μl.
- The final enzyme concentration was determined empirically and varied based on the particular substrate used. In our case, between 1 μM and 2 μM final enzyme concentrations were used to determine relative substrate specificity, and between 1 nM and 2 μM - to calculate the enzyme kinetics. For further specifics, please see Goodlett et al. (1995).
- The molar concentration of enzyme used was kept at 10% or less of the initial substrate concentration.
- The final enzyme concentration was determined empirically and varied based on the particular substrate used. In our case, between 1 μM and 2 μM final enzyme concentrations were used to determine relative substrate specificity, and between 1 nM and 2 μM - to calculate the enzyme kinetics. For further specifics, please see Goodlett et al. (1995).
- Assay was performed at 37 °C for 1 min.
- The assay duration was chosen so that only 10% or less of the initial substrate was consumed in order to minimize the occurrence of the reverse reaction.
- To quench the assay, 40 μl of 2 M HCl was added and mixed by pipetting.
- In preparation for derivatization, 40 μl 2 M NaOH was added to neutralize the acid.
- 50 μl of the neutralized, quenched assay was transferred to a new 2 ml microfuge tube.
- 100 μl of 0.5% Marfey’s reagent in acetone was added.
- 20 μl of 1 M NaHCO3 was added to make the solution alkaline, and the contents were mixed via pipetting.
- Derivatization was performed on a heat block at 40 °C for 1 h.
- During this time, fresh 1 L HPLC buffer was prepared and passed through 0.22 μm bottle top filter every time before sample analysis.
- Also, 900 μl of 80% 0.05 M TEAP buffer (pH 3.0) and 20% acetonitrile (HPLC grade) was placed in new 2 ml microfuge tubes in preparation for the 10-fold dilution of the derivatized products.
- During this time, fresh 1 L HPLC buffer was prepared and passed through 0.22 μm bottle top filter every time before sample analysis.
- Derivatization reaction was briefly centrifuged to collect any condensation from the lid of the microfuge tube.
- Reaction was cooled at room temperature for 5 min.
- 100 μl of the reaction was mixed with the solution in step B11b to prepare a 10-fold dilution.
- The diluted derivatization reaction was passed through a PTFE 0.22 μm syringe filter and placed into an amber HPLC vial.
- Derivatization reactions should be kept in an amber vial to prevent photochemical decomposition of the absorbing chromophore (Marfey, 1984). In our case, assays were analyzed within 48 h after derivatization.
- The same procedure as above was followed (the enzyme addition was omitted.) to determine AA elution times and prepare standard curves.
- Enzyme reactions were performed in 2 ml microfuge tubes.
- HPLC analysis
- The specific column employed in our case was Waters Nova-Pak, C18 column.
- 10 μl of the diluted derivatized reaction (from step B15) was analyzed.
- Flow rate was 0.5 ml/min.
- Derivatized products were detected at 340 nm.
- Several gradients were employed for the separation of different enantiomeric pairs.
- For a description of the gradients, please refer to the methods section and supplementary material of the original publication by Radkov and Moe (2013).
- The specific column employed in our case was Waters Nova-Pak, C18 column.
- Data analysis
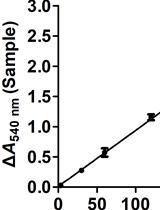
- Due to differences in the derivatization efficiency between enantiomeric pairs, derivatized D-AAs yield a higher UV response relative to L-AAs. The data provided by Goodlett et al. was used to adjust for these differences before preparing standard curves and calculating specific activities.
- Example chromatogram
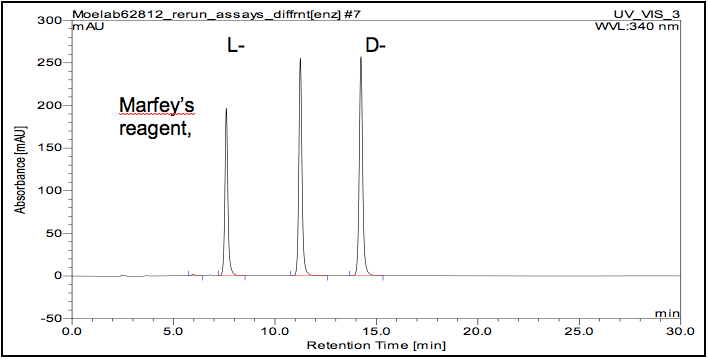
- Example chromatogram
- The Solver function in Microsoft Excel was used to perform non-linear curve fitting to the Michaelis-Menten equation.
- An example dataset (attached here) is provided as a supplementary file.
- An example dataset (attached here) is provided as a supplementary file.
- Due to differences in the derivatization efficiency between enantiomeric pairs, derivatized D-AAs yield a higher UV response relative to L-AAs. The data provided by Goodlett et al. was used to adjust for these differences before preparing standard curves and calculating specific activities.
Recipes
- HPLC buffer (0.05 M TEAP buffer, pH 3.0)
Solution of 0.05 M triethylamine was prepared and the pH was adjusted using concentrated phosphoric acid.
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from Radkov and Moe, (2013). This work was supported in part by grant 2011-67020-30195 from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
References
- Goodlett, D. R., Abuaf, P. A., Savage, P. A., Kowalski, K. A., Mukherjee, T. K., Tolan, J. W., Corkum, N., Goldstein, G. and Crowther, J. B. (1995). Peptide chiral purity determination: hydrolysis in deuterated acid, derivatization with Marfey's reagent and analysis using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 707(2): 233-244.
- Marfey, P. (1984). Determination ofD-amino acids. II. Use of a bifunctional reagent, 1, 5-difluoro-2, 4-dinitrobenzene. Carlsberg Res Communi 49(6): 591-596.
- Radkov, A. D. and Moe, L. A. (2013). Amino acid racemization in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. J Bacteriol 195(22): 5016-5024.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Radkov, A. D. and Moe, L. A. (2014). Amino Acid Racemase Enzyme Assays. Bio-protocol 4(9): e1112. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1112.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link