- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Development of a Novel Assay for Synthesis and Hydrolysis of Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate (SBP) in vitro by Combinations of Purified Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolases (FBA) Proteins and Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatases (FBPase) Proteins from Bacillus methanolicus MGA3
Published: Vol 4, Iss 14, Jul 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1186 Views: 8903
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Characterization of Protein Domain Function via in vitro DNA Shuffling
Kathy Hiu Laam Po [...] Sheng Chen
Jun 5, 2018 5264 Views
In vitro and in vivo Assessment of Protein Acetylation Status in Mycobacteria
Krishna K. Singh [...] Deepak K. Saini
Jul 5, 2019 4466 Views
In vitro Glutamylation Inhibition of Ubiquitin Modification and Phosphoribosyl-Ubiquitin Ligation Mediated by Legionella pneumophila Effectors
Alan G. Sulpizio [...] Yuxin Mao
Nov 5, 2020 2308 Views
Abstract
Bacillus methanolicus (B. methanolicus) is a Gram-positive, thermotolerant, and facultative methylotrophic bacterium that can use the one-carbon (C1) compound methanol as a source of carbon and energy (Schendel et al., 1990; Arfman et al., 1997; Arfman et al., 1992). B. methanolicus uses the Ribulose monosphosphate (RuMP) cycle for the fixation of formaldehyde (Anthony, 1986; Brautaset et al., 2007). In the RuMP cycle, Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphoasphate (SBP) can be produced from erythrose 4-phosohate (E4-P) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) by sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate aldolase (SBA) and dephosphorylated to yield sedoheptulose 7-phosphate (S7-P) by sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphatase (SBPase). Unfortunately, since neither E4-P nor SBP is commercially available, these compounds cannot be used directly in enzyme assays to obtain evidence for synthesis and hydrolysis of SBP. To circumvent this limitation, a coupled discontinuous enzyme assay including transketolase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) was used. E4-P and xylulose 5-phosphate (XU5-P) were generated from fructose 6-phosphate (F-6P) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP) by transketolase from S. cerevisiae. Aldol condensation of E-4P with DHAP to yield SBP was tested by using purified fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBAC or FBAP) from B. methanolicus (Stolzenberger et al., 2013a). Subsequently, hydrolysis of SBP to S7-P was assayed by using purified fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (GlpXC or GlpXP) from B. methanolicus (Aldolases and phosphatases are not commercially available.) (Stolzenberger et al., 2013b).
Keywords: Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate aldolaseMaterials and Reagents
- Transketolase (TKT) from S. cerevisiae (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Purified proteins: Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (GlpXC) and promiscuous fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase/Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphatase (GlpXP), as well as promiscuous fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase/ Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate aldolase (FBAC and FBAP) from B. methanolicus MGA3
- Sephadex G25 gel filtration (Amersham Biosciences )
- Factor Xa (Novagen)
- *(1 M) 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)
- *(400 mM) 20 mM D-fructose 6-phosphate dipotassium salt (F6-P) (Sigma-Aldrich)
- *(400 mM) 20 mM DL-glyceraldehyd 3-phosphate solution (GAP) (Sigma-Aldrich)
- *(400 mM) 20 mM dihydroxyacetone phosphate dilithium salt (DHAP)
- *(200 mM) 10 µM thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) (Sigma-Aldrich)
- *(40 mM) 2 mM MnCl2
- *(200 mM) 10 mM ammonium bicarbonate solution (pH 9.3)
Note: *Concentration of stock solution are given in brackets.
Equipment
- Amicon Ultra-0.5 centrifugal filter (Millipore)
- LaChromUltra HPLC system (Hitachi)
- MicroTOF-Q hybrid quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometer (BD)
- SeQuant ZIC-pHILLIC column (150 x 2.1 mm) (Merck KGaA)
Software
- Compass software 1.3 (BD)
Procedure
- Enzyme assays for the purified GlpX proteins in vitro
- The FBA activity in the direction of SBP synthesis was done by using a discontinuous, coupled enzyme assay containing TKT (from S. cerevisiae), recombinant GlpXC and GlpXP, as well as FBAC and FBAP from B. methanolicus as described below.
- Because E4-P is not acquired by purchase, E4-P was generated in a pre-reaction by the TKT (5 U/mg) from F6-P and GAP.
- Protein production and purification was done as follows:
- The enzymes were cloned into pET16b, which allows IPTG-inducible expression with an N-terminal decahistidyl tag and a factor Xa cleavage site in Escherichia coli (E. coli) BL21 (DE3).
- The induction with 0.5 mM IPTG was started at an OD600 of 0.5 to 0.6 in LB. The cells (500 ml) were harvested 4 h after induction and washed in 20 mM Tris, 300 mM NaCl, 5 mM imidazol, and 5% (vol/vol) glycerol.
- Pelleted cells were stored at 20 °C until protein purification.
- Prior to lysis by French press, cells were resuspended in 20 mM Tris, 300 mM NaCl, 5 mM imidazol, and 5% (vol/vol) glycerol, and protease activity was inhibited by addition of 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) and 1 mM diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP).
- The extract was cleared by centrifugation for 1.5 h at 140,000 x g.
- Peak fractions of Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) agarose affinity chromatography eluted with 20 mM Tris, 300 mM NaCl, 100, 200, or 400 mM imidazol, and 5% (vol/vol) glycerol were pooled, and the pooled fractions were desalted using Sephadex G25 gel filtration and buffered in 50 mM Tris/HCl (pH 7.5).
- After purification, the His tag was cleaved by factor Xa according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- The purified protein was buffered in 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5). The reaction mixture contained 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 20 mM F6-P, 20 mM GAP, 20 mM DHAP, 10 µM thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), 2 mM MnCl2 and 3 U/mg of each purified enzyme (FBAC or FBAP and GlpXC or GlpXP).
- The reaction was started by addition of TKT (5 U/mg). The detection of the generated products was performed via liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) as described below.
- The assay was performed at 50 °C for 45 min in volume of 1 ml. The reaction was stopped by purification of the containing enzymes using Amicon Ultra-0.5 centrifugal filter. Therefore, the reaction mixture was sampled to the Amicon® Ultra filter device and cap it and the device was centrifuged at 14,000 x g for approximately 30 min. Thereby the proteins were filtered out of the mixture but the remaining incredients passed. The supernatant was then free of protein and the incredients were analyzed by LCMS. The expectations and results and described in a separate section below.
- The FBA activity in the direction of SBP synthesis was done by using a discontinuous, coupled enzyme assay containing TKT (from S. cerevisiae), recombinant GlpXC and GlpXP, as well as FBAC and FBAP from B. methanolicus as described below.
- LC-MS analysis of the products after enzyme assay
- LC-MS data were obtained using a LaChromUltra HPLC system coupled to a microTOF-Q hybrid quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometer.
- For Ionization the mass spectrometer is equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source. Separation of the samples via HPLC was carried out by a SeQuant ZIC-pHILLIC column using the solvents 10 mM ammonium bicarbonate solution (pH 9.3) as eluent A and acetonitrile as eluent B.
- The injection volume was 2 µl, flow rate was set to 150 µl min-1, and gradient elution was performed as follows: t = 0 min, 80% B; t = 30 min, 10% B; t = 35 min, 10% B; t = 40 min 80% B; t = 60 min 80% B.
- MS detection was performed via ESI source in negative ionization mode. Nitrogen was applied as sheath, dry and collision gas.
- For internal mass calibration a solution of formate (0.1 M) in 50 % (v/v) isopropanol was injected within each MS analysis.
- MSMS analyses were performed by the auto MSMS mode of the microTOF-Q.
Table 1. Parameters for microTOFcontrol in full scan MS modeMode Scan Mode
Mass Range
Spectra Acquisition
Include Profile Spectra
FocusMS
50-1000 m/z
Save Spectra
Always
InactiveIon Polarity
Rolling Average
Absolute Threshold
Peak Summation Width
Acquisition RatePositive
off
10
5 pts
1.0 HzSource Endplate Offset
Capillary
Nebulizer-500 V
+ 4500 V
2.0 barDry Gas
Dry Temp8.0 L / min
180 °CTransfer Funnel 1 RF
Funnel 2 RF300.0 Vpp
300.0 VppISCID Energy
Hexapole RF0.0 eV
200.0 VppQuadrupole Ion Energy 4.0 eV Low Mass 150.00 m/z Collision Cell Collision Energy
Transfer Time8.0 eV
75.0 µsCollision RF
Pre Puls Storage130.0 Vpp
5.0 µs - Raw data were analyzed using the Compass software 1.3. Automatic internal mass calibration was achieved using the HPC quadratic algorithm.
- Identification of compounds was performed either by the specific mass to charge ratio and the retention time or by comparing the fragment ions in MSMS mode.
Table 2. Additional parameters for microTOFcontrol in MS/MS (MRM) modeAuto MSMS Precursor Ions 3 Threshold 6000
countsTransfer Funnel 1 RF
Funnel 2 RF300.0 Vpp
300.0 VppISCID EnergyHexapole RF 0.0 eV
200.0 VppQuadrupole Ion Energy 4.0 eV Low Mass 150.00 m/z Collision Cell Collision Energy
Transfer Time8.0 eV
75.0 µsCollision RF
Pre Puls Storage130.0 Vpp
5.0 µs
- LC-MS data were obtained using a LaChromUltra HPLC system coupled to a microTOF-Q hybrid quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometer.
Notes about results/experimental setup
- The assay was performed to detect the synthesis and hydrolysis of SBP in vitro by combinations of purified FBA proteins and FBPase proteins from B. methanolicus MGA3. In the SBPase variant of the RuMP cycle, SBP is produced from E4-P and DHAP by SBA and dephosphorylated to yield S7-P by SBPase. Unfortunately, since neither E4-P nor SBP is commercially available, these compounds cannot be used directly in enzyme assays to obtain evidence for synthesis and hydrolysis of SBP. To circumvent this limitation, a coupled discontinuous enzyme assay including transketolase from S. cerevisiae was used.
- Various combinations of substrates and enzymes were tested (Figure 1). No evidence for instabilities of the sugar phosphates at 50 °C was obtained when the substrates were incubated without enzymes.
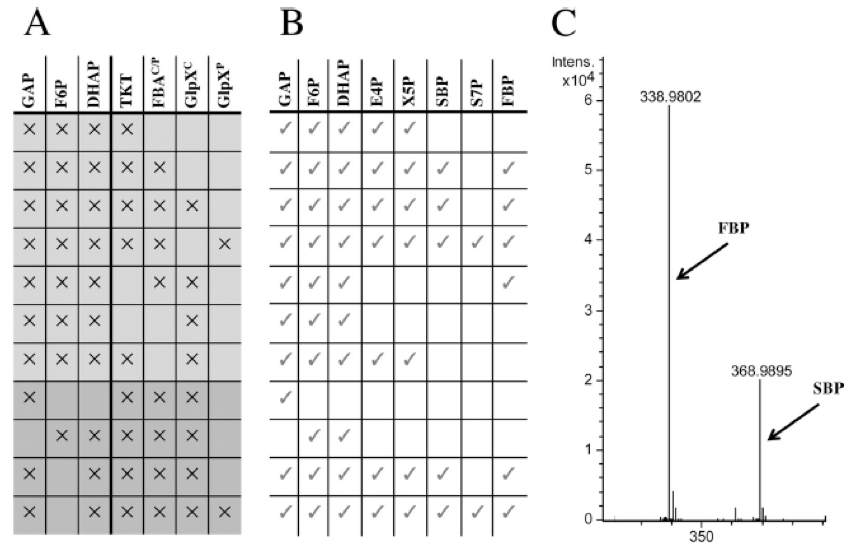
Figure 1. Determination of the sugar phosphate intermediates of the RuMP cycle using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Shown is the experimental setup and determination of the sugar phosphate intermediates of the RuMP cycle using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). For the identification of sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, MS/MS was used. (A) Scheme of the substrate and enzyme combinations used in the assay. X indicates presence in the assay. (B) Presence (check marks) or absence of the indicated sugar phosphates, as detected by LC-MS/MS analysis. (C) LC-MS spectra of FBP and SBP. - E4-P and xylulose 5-phosphate (XU5-P) were generated from F-6P and GAP by transketolase from S. cerevisiae (Figure 1, line 1). Aldol condensation of E-4P with DHAP to yield SBP could be detected for both purified FBAC or FBAP from B. methanolicus (Figure 1, line 2). LC-MS/MS analysis confirmed the identity of SBP, which showed the expected mass shift of 30 Da (-CHOH-) compared to FBP (Figure 1, C). Thus, these results indicated that both FBAs from B. methanolicus are active as SBAs in vitro. Subsequently, hydrolysis of SBP to S7-P was assayed by using purified GlpXC or GlpXP from B. methanolicus. Hydrolysis of SBP and formation of S7-P occurred only when GlpXP, but not GlpXC, was added (Figure 1, line 3, 4). Thus, for the major FBPase of B. methanolicus, GlpXC, evidence for SBPase activity could not be obtained in vitro, while GlpXP showed activity as an SBPase.
Abbreviations
Enzymes
FBA fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.13)
TKT transketolase (EC 2.2.1.1)
GlpX fructose-bisphosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1)
SBA sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.x)
SBPase sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate (EC 3.1.3.37)
Metabolites
F6-P fructose-6-phosphate
FBP fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
GAP glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
DHAP dihydroxyacetone phosphate
E4-P erythrose 4-phosphate
SBP sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate
S7-P sedoheptulose-7-phosphate
Ri5-P ribose 5-phosphate
X5P xylulose 5-phosphate
Ru5P ribulose 5-phosphate
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Dr Trygve Brautaset for providing the strain B. methanolicus MGA3 and the plasmid pTH1; Dr Sonja Siwiora Brenke for providing the facilities, equipment and technical assistance to perform size exclusion chromatography and molecular mass estimation of the purified protein. This work was supported by SynMet, a 09-EuroSYNBIO-FP-023 project, funded in part by DFG through grant no. WE 2320/2-1.
References
- Anthony, C. (1986). Bacterial oxidation of methane and methanol. Adv Microb Physiol 27: 113-210.
- Arfman, N., Hektor, H. J., Bystrykh, L. V., Govorukhina, N. I., Dijkhuizen, L. and Frank, J. (1997). Properties of an NAD(H)-containing methanol dehydrogenase and its activator protein from Bacillus methanolicus. Eur J Biochem 244(2): 426-433.
- Arfman, N., Dijkhuizen, L., Kirchhof, G., Ludwig, W., Schleifer, K. H., Bulygina, E. S., Chumakov, K. M., Govorukhina, N. I., Trotsenko, Y. A., White, D. and et al. (1992). Bacillus methanolicus sp. nov., a new species of thermotolerant, methanol-utilizing, endospore-forming bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42(3): 439-445.
- Brautaset, T., Jakobsen, O. M., Josefsen, K. D., Flickinger, M. C. and Ellingsen, T. E. (2007). Bacillus methanolicus: a candidate for industrial production of amino acids from methanol at 50 degrees C. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74(1): 22-34.
- Lindner, S. N., Vidaurre, D., Willbold, S., Schoberth, S. M. and Wendisch, V. F. (2007). NCgl2620 encodes a class II polyphosphate kinase in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(15): 5026-5033.
- Schendel, F. J., Bremmon, C., Flickinger, M., Guettler, M. and Hanson, R. (1990). L-lysine production at 50 degrees C by mutants of a newly isolated and characterized methylotrophic Bacillus sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(4): 963-970.
- Stolzenberger, J., Lindner, S. N. and Wendisch, V. F. (2013a). The methylotrophic Bacillus methanolicus MGA3 possesses two distinct fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolases. Microbiol 159(Pt 8): 1770-1781.
- Stolzenberger, J., Lindner, S. N., Persicke, M., Brautaset, T. and Wendisch, V. F. (2013b). Characterization of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase and sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphatase from the facultative ribulose monophosphate cycle methylotroph Bacillus methanolicus. J Bacteriol 195(22): 5112-5122.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Stolzenberger, J., Lindner, S. N., Persicke, M., Brautaset, T. and Wendisch, V. F. (2014). Development of a Novel Assay for Synthesis and Hydrolysis of Sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate (SBP) in vitro by Combinations of Purified Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolases (FBA) Proteins and Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatases (FBPase) Proteins from Bacillus methanolicus MGA3. Bio-protocol 4(14): e1186. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1186.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein
Biochemistry > Protein > Synthesis
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link