- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
In vitro Assay for Cytidine Deaminase Activity of APOBEC3 Protein
Published: Vol 4, Iss 20, Oct 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1266 Views: 12251
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
In vitro Nitrate Reductase Activity Assay of Mycolicibacterium smegmatis Crude Extract
Wei Tan [...] Guo-Ping Zhao
Jul 20, 2021 2098 Views
Assay for Protealysin-like Protease Inhibitor Activity
Igor M. Berdyshev [...] Ilya V. Demidyuk
Oct 5, 2022 701 Views
H2 Production from Methyl Viologen–Dependent Hydrogenase Activity Monitored by Gas Chromatography
Nuttavut Kosem
Dec 5, 2023 130 Views
Abstract
Cytidine deaminases are enzymes that catalyze the removal of an amino group from cytidine, forming uridine. APOBEC3 (ApolipoproteinB mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide like) proteins are cytidine deaminases that deaminate cytidines in polynucleotides (RNA/DNA), resulting in editing of their target substrates. Mammalian APOBEC3 proteins are an important element in cellular defenses against retrovirus replication, and this “restriction” of retroviral infections is partially due to the cytidine deaminase activity of the APOBEC3.The present protocol (Nair et al., 2014) describes the assay to detect the deaminase activity of mouse APOBEC3 protein, which targets cytidines present in TCC or TTC motifs in a single-stranded DNA substrate. In brief, the protein preparation to be assayed is incubated with a fluorophore-labeled oligodeoxynucleotide containing the deamination target motif (radiolabeled oligonucleotide substrates have also been successfully used by other groups). Cytidines in the oligonucleotide are deaminated to uridines; the addition of Uracil DNA Glycosylase (UDG) catalyzes the hydrolysis of the N-glycosylic bond between uracil and sugar, generating an abasic (AB) site in the oligonucleotide. Mild alkali treatment cleaves the substrate oligonucleotide at the AB site; cleaved products are resolved from uncleaved substrate by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and visualized on a fluorescence scanner.
The protocol described here is mainly adapted from that described by Iwatani et al. (2006) with modifications. The assay can, of course, be used to detect the activity of other APOBEC3 deaminases targeting DNA substrates, using oligonucleotides containing the cytidine-containing target sequence for the deaminase.
Materials and Reagents
- 5’ N-AlexaFluor488-labeled oligodeoxynucleotide (custom synthesized from Integrated DNA Technologies)
Example: 5' -/5Alex488N/ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA TCC ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA-3’, PAGE purified, 250 nmol synthesis scale (see Recipes) (while a 48-base oligodeoxynucleotide is described here, both longer and shorter oligodeoxynucleotides could undoubtedly be used). - Nuclease-free or autoclaved sterile water
- 1 U/µl Uracil DNA glycosylase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EN0361 )
- 0.6 N NaOH
- 2x RNA loading dye (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: R0641 )
- 10 bp DNA ladder (Life Technologies, catalog number: 10821-015 )
- Tris (Sigma-Aldrich)
- NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich)
- DTT (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Novex® TBE-UREA gel (Life Technologies, catalog number: EC6885BOX/EC68852BOX )
- Boric acid
- EDTA
- 10x deaminase buffer (see Recipes)
- 10x Uracil DNA glycosylase reaction buffer (see Recipes)
- 10x Tris borate EDTA (TBE) buffer (see Recipes)
- N-AlexaFluor labelled oligodeoxynucleotides (see Recipes)
Equipment
- RNase- and DNase-free 0.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes
- 37 °C water bath
- Heating Block set to 95 °C
- XCellSureLock® Mini-Cell Electrophoresis apparatus (Life Technologies, catalog number: EI0001 )
- Powerpac Basic Power Supply (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 164-5050 )
- Typhoon Imager (Trio+, variable mode imager) (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 2340730 )
Procedure
- Set up 10 µl deaminase assay reactions in 0.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes as follows. First prepare a deaminase assay Master Mix, with enough volume for all of the reactions plus some excess. The table below gives the recipe for a Master Mix for 10 reactions, although enough Master Mix (99 µl) is prepared for 11 reactions:
Deaminase assay components Amount per reaction Master mix Water 7.5 µl 82.5 µl 10x deaminase buffer 1 µl 11 µl Fluorophore-labeled oligonucleotide substrate (10 pmol/µl) 0.5 µl 5.5 µl
Dispense 9 µl of the Master Mix into each tube; then add 1 µl of the protein preparation to be assayed to each tube. In our experience, approximately 0.25 µg of mouse APOBEC3 is sufficient for deamination of a large fraction of the oligodeoxynucleotide substrate in this assay. (A no-protein, “blank” control reaction should also be prepared to which protein buffer, instead of protein, is added.)
Gently mix the reactants by pipetting up and down, and if required, give a quick spin to collect all the contents at the bottom of the tube. Incubate the reaction in a 37 °C water bath for 2 h.
Note: During the 2 h incubation at 37 °C, centrifuge the contents of the tubes at low speed occasionally as moisture tends to accumulate at the tube caps owing to evaporation. - Prepare UDG Master Mix as indicated in the table below. For example, if 10 assays are being performed, prepare 55 µl UDG Master Mix, i.e., enough for 5 µl/reaction + 5 µl excess volume:
UDG enzyme mix Amount per reaction Master mix Water 2.75 µl 30.25 µl 10x UDG buffer 1.5 µl 16.5 µl UDG enzyme (1 U/µl) 0.75 µl 8.25 µl
Add 5 µl of this UDG Master Mix to the 10 µl deaminase assay reaction tubes from step 1. Gently mix the reactants and incubate in the 37 °C water bath for 45 min. - Following the 45 min incubation, add 5 µl of 0.6 N NaOH to each tube and incubate further at 37 °C for 20 min.
- Add an equal volume (20 µl) of 2x RNA loading dye to each tube, heat at 95 °C for 2-3 min, and place on ice immediately.
- Load 15 µl of each sample onto a 15% TBE-UREA PAGE gel and resolve the cleaved and uncleaved products by electrophoresis at 150 volts for 3 h at room temperature (25 °C) in 1x TBE buffer. (Before loading the samples, flush the wells with running buffer using a syringe fitted with a needle. This removes residual urea or acrylamide from the wells and minimizes the probability of samples smearing on the gel.)
- In order to visualize the uncleaved substrate and cleaved product(s), remove the gel carefully from the cast, slice away the sealing gel end at the bottom, and place the gel onto a clean glass plate. Carefully place a cling film/saran wrap on the gel; remove any air bubbles between the gel and the film by gently rolling a roller (supplied with the gel apparatus) or a Pasteur pipette over it. Air bubbles tend to interfere with the fluorescence imaging. A trick to avoid air bubbles and to keep the gel from drying and breaking is to generously put several drops of water on the gel before placing the cling film.
- Place the gel on the fluorescence reader, gel side facing the scanner and glass side up. The scanner should be set for AlexaFluor 488 (excitation 495 nm, Emission 519 nm), PMT 600, sensitivity normal, and scanning speed 200 microns.
Representative data
- A representative gel is shown in Figure 1. In general we have found this assay to be extremely robust and reproducible.
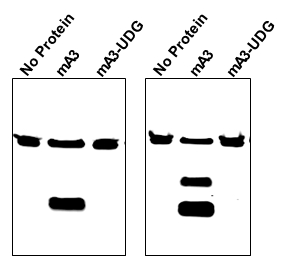
Figure 1. Mouse APOBEC3 was tested with two 48-base oligodeoxynucleotides. The first (left panel) was composed entirely of A and T residues, except for residues 25-27, which were TTC, and which was labeled with AlexaFluor 488 at its 5’ end. The oligonucleotide was incubated with no protein (first lane) and with mouse APOBEC3 produced in Sf9 cells (second and third lanes). The second lane shows the results of this incubation, followed by the full assay protocol described here, while the third lane shows the results when UDG was omitted from the assay. The right panel shows a similar assay, but the oligonucleotide contained, in addition to A and T residues, TCCC at residues 21-24 and TTCC at residues 28-31.
Notes
- While the assay we have described here monitors the deamination of a substrate oligodeoxynucleotide with a fluorophore at its 5’ end, many investigators have used 5’- 32P-labeled oligodeoxynucleotides instead, measuring the cleavage by autoradiography rather than fluorescence imaging. Some researchers may find this more convenient or economical than the use of fluorescence. However, the principles and most of the procedures used in the two methods are identical.
- As a positive control on the assay, one can design an oligonucleotide identical to the substrate (Materials and Reagents) except that it contains uracil rather than cytosine (5' - /5Alex488N/ ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA TUU ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA ATA 3’). This should be completely cleaved in the UDG-alkali treatments; if it is not, this is an indication that the treatments are not successful in inducing cleavage at all deoxyuridines in the oligodeoxynucleotides.
- The protocol here (“Procedure”, text of step 1) calls for the addition of 1 µl of the protein preparation to be assayed for deaminase activity. Our preparations (Nair et al., 2014) were partially purified from Sf9 insect cells and typically contained 0.5-1 µg of protein per µl.
Recipes
- 10x deaminase buffer
100 mM Tris.HCl (pH 8.0)
500 mM NaCl
10 mM DTT
Note: Tris, NaCl and DTT were all procured from Sigma Aldrich. Stock solutions of 1 M Tris HCl (pH 8.0) and 5 M NaCl were autoclaved and stored at RT, while 1 M DTT solution was freshly made and was stored at -20 °C.
10x deaminase buffer (1 ml) Volume (µl) 1 M Tris.HCl (pH 8.0) 100 5 M NaCl 100 1 M DTT 10 Water 790
This buffer should be stored at -20 °C. - 10x Uracil DNA glycosylase reaction buffer
200 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.2 at 25 °C)
10 mM EDTA
100 mM NaCl
Supplied with Uracil DNA glycosylase - 10x Tris borate EDTA (TBE) buffer
108 g Tris base
55 g boric acid
40 ml 0.5 M EDTA (pH ~8.3) - N-AlexaFluor labelled oligodeoxynucleotides
These are supplied as dried powder/pellet/precipitate. Dissolve in nuclease-free or autoclaved sterile water to a final concentration of 1 nmol/µl stock. Stored at -20 °C, in dark tubes. In order to avoid repeated freezing and thawing of the substrate it is advisable to make several aliquots of 50 µl each of a working concentration of 10 pmol/µl and store at -20 °C in dark tubes. Although the yield of the oligodeoxynucleotides is generally only 2-5% of the scale of synthesis, it may well be sufficient for the assays as each assay reaction only consumes 5 pmol or even less.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jennifer Miller and Jason Rausch for help with the assay. This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, Center for Cancer Research.
References
- Iwatani, Y., Takeuchi, H., Strebel, K. and Levin, J. G. (2006). Biochemical activities of highly purified, catalytically active human APOBEC3G: correlation with antiviral effect. J Virol 80(12): 5992-6002.
- Nair, S., Sanchez-Martinez, S., Ji, X. and Rein, A. (2014). Biochemical and biological studies of mouse APOBEC3. J Virol 88(7): 3850-3860.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Nair, S. and Rein, A. (2014). In vitro Assay for Cytidine Deaminase Activity of APOBEC3 Protein. Bio-protocol 4(20): e1266. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1266.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link