- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Phakopsora pachyrhizi Infection Bioassay in Detached Soybean Transgenic Leaves for Candidate Gene Validation
Published: Vol 5, Iss 14, Jul 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1540 Views: 8324
Reviewed by: Arsalan DaudiKanika GeraAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Quantification of the Composition Dynamics of a Maize Root-associated Simplified Bacterial Community and Evaluation of Its Biological Control Effect
Ben Niu and Roberto Kolter
Jun 20, 2018 8260 Views
Tracking Root Interactions System (TRIS) Experiment and Quality Control
Hassan Massalha [...] Asaph Aharoni
Apr 20, 2019 5749 Views

A Quick Method for Screening Biocontrol Efficacy of Bacterial Isolates against Bacterial Wilt Pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum in Tomato
Heena Agarwal [...] Niraj Agarwala
Nov 20, 2020 3909 Views
Abstract
Soybean (Glycine max) is one of the most important crops in the world. Phakopsora pachyrhizi is a plant pathogenic basidiomycete fungus that infects soybean, causing Asian Soybean Rust (ASR) disease and affecting production. Here, we describe how to prepare the plant material and the uredospore suspension (from spores harvested from leaves exhibiting sporulating uredinia) for in vitro leaf infection. Plant material is sprayed with the uredospore suspension and incubated for 12 days. During the incubation period, the presence of lesions and pustules is visually verified. After this incubation period, the leaves are classified according to the lesion type. The number of uredospores per CM2 of leaf was also estimated. The detached-leaf assay is routinely used to test fungicide efficiency (Scherb and Mehl, 2006). Detached-leaf, greenhouse and field results have been shown to be significantly correlated (Twizeyimana et al., 2007). The present protocol was adapted from the two publications cited above. The usefulness of this approach for studying P. pachyrhyzi infection on transgenic soybean was previously demonstrated by our research team (Wiebke-Strohm et al., 2012; Bencke-Malato et al., 2014).
Materials and Reagents
- Soybean transgenic and non-transgenic plants of similar age
- Leaves infected with Phakopsora pachyrhizi uredospores (Figure 1A)
- Tween 20 (Labsynth)
- Uredospore suspension (see Recipes)
Figure 1. Soybean response to rust infection on the abaxial leaf surface. A. Tan, B. reddish brown and (C) immune.
Equipment
- Petri dish (Ø 9 cm)
- Hand sprayer that can be adjusted for spraying 1 ml volume (Figure 2A and 2B, Video 1)
- Plant culture room
- Growth chamber
- Stereomicroscope
- Laminar flow sterile cabinet
- Neubauer chamber

Figure 2. Hand sprayer
Procedure
- Leaves infected with Phakopsora pachyrhizi uredospores were randomly sampled in the field. Alternatively, uredospores of a determined isolate were propagated on plants under greenhouse conditions. Immediately after sampling, leaves were stored in a dry plastic or paper bag at room temperature up to four days. However, better results are expected from material recently collected or stored under refrigeration.
In the laboratory, uredospores were tapped off of the leaves into a suitable dry tube using a paint-brush, as shown in Video 2. This step should be done a short time before inoculation, that means, the time necessary to carry out 3-5 steps. The amount of uredospores depends on the amount of leaves that will be included in the experiment. To have an estimate please see steps 3 and 6.Video 2. Uredospores tapped off of the leaves using a paint-brush - Fifty ml uredospore suspension was prepared using sterile distilled water, 1 drop of Tween 20 and uredospores to a final concentration of 1 x 105 spores/ml. The concentration of uredospores was estimated using a Neubauer chamber. The Tween 20 was added using a pipette, as shown in Video 3. Fifty ml solution can be used to infect approximately 50 leaves. Video 3. One drop of Tween 20 using a 1 ml pipette
- Soybean transgenic and non-transgenic plants were cultivated in a plant culture room at 26 ± 1 °C with a 16/8 h light/dark cycle at a light intensity of 22.5 µE/m2/s. Fully expanded trifoliate leaves with similar size and position were collected from plants of the same age. The newest fully expanded leaf of 2-month-old plants (V5 or V6 stages) was preferentially used, but plants in other growth stages may be also used.
- From this step forward, the material was aseptically manipulated in a laminar flow cabinet. The leaves were rinsed (quick submersion) in sterile distilled water and rapidly dried on sterile filter paper. Each leaflet was cut into 5 cm x 5 cm pieces and individually placed with the abaxial side upwards in a sterile Petri dish (Ø 9 cm) containing filter paper saturated with distilled water to maintain high humidity (Figure 3).

Figure 3. Soybean leaf piece with the abaxial surface upwards in a Petri dish containing filter paper saturated with water - Each leaf piece was inoculated by spraying 1 ml of the uredospore suspension (105 spores/ml). The uredospore suspension was mixed immediately before each inoculation. A distance of 10 cm was maintained between the hand sprayer and the leaf piece.
- The Petri dishes were incubated in a growth chamber at 20 °C with a 12/12 h light/dark cycle for 12 days.
- The material was visually evaluated for the presence of lesions and pustules every 2 days during the incubation period.
- After 12 days of incubation, leaves showing signals of other diseases or rotting were eliminated (Figure 4). The remaining material was visually classified according to the lesion type (immune, reddish brown or tan) present on the abaxial side of the leaf (Figure 1). Additionally, the number of lesions, the number of lesions with pustules, the number of pustules per lesion, the total number of pustules and the total number of opened pustules present on each leaf piece was recorded under a stereomicroscope (see Note 4; Figure 5). Finally, two infected areas of 1 cm x 1 cm were determined in each leaf piece and cut off. Each 1 cm2 piece was placed in a microtube containing 500 µl water and vortexed vigorously for 1 min. The mean number of uredospores per cm2 was estimated under a stereomicroscope using a Neubauer chamber.

Figure 4. Examples of leaves showing signals of other diseases or rotting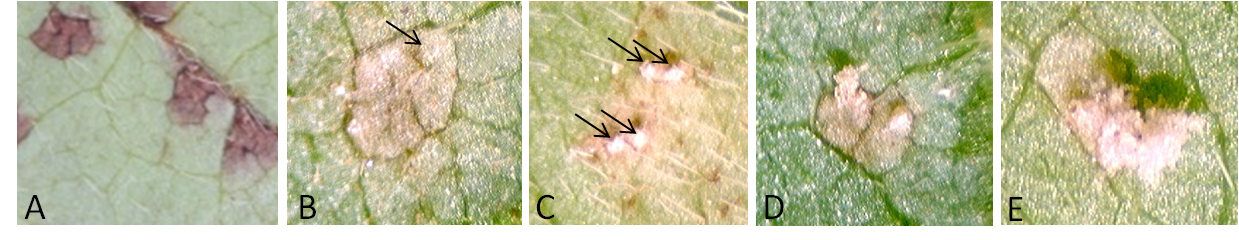
Figure 5. Parameters used to compare genotype response to rust infection. A. Lesions without pustule; B. lesion with one pustule (indicated by an arrow); C. lesion with multiple pustules (indicated by arrows); D. a cone-shaped opened pustule (left) and a cone-shaped unopened pustule (right); E. a cone-shaped opened pustule with a pore on the top and spores inside (left) and an opened pustule with spores on top of the cone (right). - Results obtained from each leaf piece were considered replicates. Tree leaf pieces from the same plant and at least two plants from each transgenic event were used.
- Non-transformed plants of the same genetic background were used as a control. Ideally, a susceptible and a partially resistant variety should be used as positive and negative controls of the experimental conditions.
Notes
- Whenever possible the material should be aseptically manipulated to avoid cross contamination.
- Twizeyimana et al. (2007) placed the leaves on medium. We were not able to establish the protocol using the same medium due to cross contamination and rotting.
- The use of intact leaves will help to prevent cross contamination and rotting. However, bigger Petri dishes and more space in growth chambers will be necessary to carry out the experiment.
- Rust symptoms begin as small lesions on the abaxial leaf surface that gradually increase in size and change from gray to tan or reddish brown. Soybean rust produces two types of lesions: tan (Figure 1A) and reddish brown (Figure 1B). When mature, tan lesions consist of small pustules surrounded by slightly discolored necrotic area with masses of tan spores (Figure 5B-E). Reddish brown lesions have a larger reddish brown necrotic area, with a limited number of pustules and few visible spores. The mature soybean rust pustules are cone-shaped with a pore on the top and spores inside or on the cone (Figure 5D-E). (http://www.aphis.usda.gov/publications/plant_health/content/printable_version/Soybean_Rust_22.pdf).
Recipes
- Uredospore suspension
P. pachyrhizi uredospores, 1 drop of Tween 20 (Video 2) and sterile distilled water to a final concentration of 1 x 105 spores/ml.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Emerson M. Del Ponte, Dr. Juliano dos Santos and Larissa Bittecourt for their technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS). The present protocol was adapted from Scherb and Mehl (2006) and Twizeyimana et al. (2007).
References
- Bencke-Malato, M., Cabreira, C., Wiebke-Strohm, B., Bucker-Neto, L., Mancini, E., Osorio, M. B., Homrich, M. S., Turchetto-Zolet, A., De Carvalho, M., Stolf, R., Weber, R., Westergaard, G., Castagnaro, A. P., Abdelnoor, R. V., Marcelino-Guimaraes, F. C., Margis-Pinheiro, M. and Bodanese-Zanettini, M. (2014). Genome-wide annotation of the soybean WRKY family and functional characterization of genes involved in response to Phakopsora pachyrhizi infection. BMC Plant Biol 14(1): 236.
- Scherb, C. T. and Mehl, A. (2006). SBI fungicides, also suited for other fungicide classes - detached leaf test. FRAC (Fungicide Resistance Action Committee)
- Twizeyimana, M., Ojiambo, P., Ikotun, T., Paul, C., Hartman, G. and Bandyopadhyay, R. (2007). Comparison of field, greenhouse, and detached-leaf evaluations of soybean germplasm for resistance to Phakopsora pachyrhizi. Plant Dis 91(9): 1161-1169.
- Wiebke-Strohm, B., Pasquali, G., Margis-Pinheiro, M., Bencke, M., Bucker-Neto, L., Becker-Ritt, A. B., Martinelli, A. H., Rechenmacher, C., Polacco, J. C., Stolf, R., Marcelino, F. C., Abdelnoor, R. V., Homrich, M. S., Del Ponte, E. M., Carlini, C. R., De Carvalho, M. C. and Bodanese-Zanettini, M. H. (2012). Ubiquitous urease affects soybean susceptibility to fungi. Plant Mol Biol 79(1-2): 75-87.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Wiebke-Strohm, B., Rechenmacher, C., Oliveira, L. A. D., Godoy, C. V. and Zanettini, M. H. B. (2015). Phakopsora pachyrhizi Infection Bioassay in Detached Soybean Transgenic Leaves for Candidate Gene Validation. Bio-protocol 5(14): e1540. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1540.
Category
Plant Science > Plant immunity > Disease bioassay
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > Fungus
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > In vivo model
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link