- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Agrobacterium rhizogenes-Based Transformation of Soybean Roots to Form Composite Plants
Published: Vol 6, Iss 2, Jan 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1708 Views: 10500
Reviewed by: Zhaohui LiuJoern KlinkenbergTeresa Lenser

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Investigation of Transposon DNA Methylation and Copy Number Variation in Plants Using Southern Hybridisation
Vivek Hari Sundar G. and P. V. Shivaprasad
Jun 5, 2022 1255 Views

Agrobacterium-mediated Genetic Transformation of Cotton and Regeneration via Somatic Embryogenesis
Alka Srivastava [...] Praveen C. Verma
May 20, 2023 1115 Views

A Plate Growth Assay to Quantify Embryonic Root Development of Zea mays
Jason T. Roberts [...] David M. Braun
Oct 20, 2023 423 Views
Abstract
Transgenic soybean roots of composite plants are a powerful tool to rapidly test the function of genes and activity of gene promoters. No tissue culture is needed, thus avoiding loss of valuable material due to contamination. This is a simple technique that requires less training and care than tissue culture techniques. Furthermore, it takes less time to produce transgenic roots than techniques using sterile tissue culture. If the transgenic roots are to be challenged with a pathogen, there is no need to produce axenic pathogens with this technique, because sterile tissue culture medium is not used. Therefore, there is no agar medium on which contaminants may grow resulting in obscured results or diseased roots. Here, we describe the production of transgenic soybean roots on 7-day-old soybean seedlings using Agrobacterium rhizogenes. These composite plants may be grown in the greenhouse for further experimentation, such as to determine the effect of gene expression on nematode development.
Materials and Reagents
- 17 x 100 mm, 14 ml culture tubes designed for bacteria
- Sodium hypochlorite (Commercial Bleach-Clorox)
- Soybean seeds (William 82) (Glycine max)
- Agrobacterium rhizogenes strain K599 (Homemade culture)
- PRAP15, pRAP17 or other plasmid
- Tetracycline hydrochloride, min. 95% (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Murashige & Skoog Medium- including vitamins (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: P08805.02 )
- Ethyl alcohol (The Warner Graham Company, Gas, catalog number: 64-17-5 )
Note: Currently, it is “Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 64-17-5 ”. - Anti-bacterial soap (Clean & smooth)
- MS salts
- 3% sucrose
- Casein digest peptone
- Yeast extract
- Dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4)
- Potassium phosphate (K3PO4)
- Glycerol
- KOH
- MS media (see Recipes)
- Terrific Broth, Modified (Research products International Corp., catalog number: 31237 ) (see Recipes)
- Fertilizer-Peters Excel 13-2-13 150 ppm nitrogen (pH 6.1) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 162 pots flat trays and 32 pot flats (Myers Lawn&Garden)
- Promix Flexible Purpose (Pro-Mix, model: Flex Loose 2.8 cuft )
- Heated growing mat (Home depot)
- 1 L culture flasks (Pyrex)
- Spectrophotometer UV-120-02 (Shimadzu Corporation, catalog number: 204-00010-08 )
- Centrifuge with a GSA rotor (model: Sorvall RC-5B Refrigerated Super speed Centrifuge)
- Plastic pasteur pipette (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 357575 )
- A desiccator attached to a vacuum pump
- G10 Gyrotory shaker (New Brunswick Scientific)
- Gyrotory water bath Shaker (LabX, New Brunswick Scientific, model: G76 )
- Buckets (Home depot)
- Growth chamber
- Stainless steel scissors (Roboz Surgical Instrument Co., catalog number: RS-5912 )
- Dark Reader Spot Lamp-SL85 (Clare Chemical Research)
- Orange filter glasses (Clare Chemical Research)
- Patio/Paver Sand. Multi-purpose (Pavestone)
- 50 ml disposable plastic beakers
- Clear plastic tub
- Rotating platform
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Nalgene Spherical-Bottom Centrifuge Bottle, Polycarbonate (PC)-Jade Scientific Inc./ NalgeneTM Spherical-Bottom Polycarbonate Centrifuge Bottle (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 3123-0250 )
- Vacuum 380 mm Hg (Torr)
Procedure
- Preparing the soybean seedlings
- Count soybean seeds as needed, approximately 162 seeds per DNA construct. Sort the seeds to remove seeds that are diseased, small, or damaged. Remove weed seeds and other extraneous material. The approximate number of soybean cv. Williams 82 seed can be determined by weight using 22.5 grams equals 100 seeds. Seeds from other soybean cultivars may have a different weight per 100 seeds. Sterilize soybean seeds by soaking in 10% bleach for 10 min. 300 ml of 10% bleach in a 1 L plastic beaker works well for up to about 300 grams of seed. Add the seed to the bleach solution, swirl briefly to sink the seeds, and allow the seeds to rest quietly for the remainder of the exposure. Pour off the bleach solution. The seeds were rinsed about 10 times in quick succession with RO [reverse osmosis] water to remove the bleach. Alternatively, run RO water into the beaker until it is full and the seeds are suspended. Continue to run the RO water into the beaker for about 20 sec. Drain the water from the seeds. Repeat 4 times. Drain the seeds well, but gently. Handle the seeds gently, as they are now fragile.
- Plant the soybean seeds 7 to 9 days before the transformation date. The seeds germinate and the seedlings grow faster in the summer and slower in the winter. In a 9 x 18 cell flat, plant 2 seeds per cell containing hydrated Promix potting media. Thus, one 8 x 18 cell flat provides enough plants (324) for two constructs. Hydrate the Promix by mixing it with water in a 5-gallon bucket.
Place the 162 cell flat on a clean surface, and fill the individual pots with the hydrated Promix, packing each pot with firm pressure, using one finger per pot. Fill with more ProMix to make it level with the top of the flat. Form a hole to plant the seed by dibbling the Promix with an extra large sharpie pen of something similar to a depth of 2 cm. Plant 2 seeds per cell; lightly cover the seeds with ProMix; and add more ProMix to cover as needed. The covering ProMix is placed lightly and not pressed. Water the seeded flats until the Promix is moderately saturated. Place the 162 pot flat directly on the growing bench or heated growing mat, without any open flats underneath. Do not water the flat again until the top layer of Promix has begun to dry to a light brown color. Water lightly, as needed, until the plants emerge (Figure 1).
Note: In the summer, in Maryland, USA, the seedlings are ready on the 7th or 8th day after planting. At this time the first cotyledonary leaves are partially open. During the winter and cooler seasons, the seedlings may not be at the correct stage until the 9th or 10th day after planting, you can use a heated germination mat in the winter season.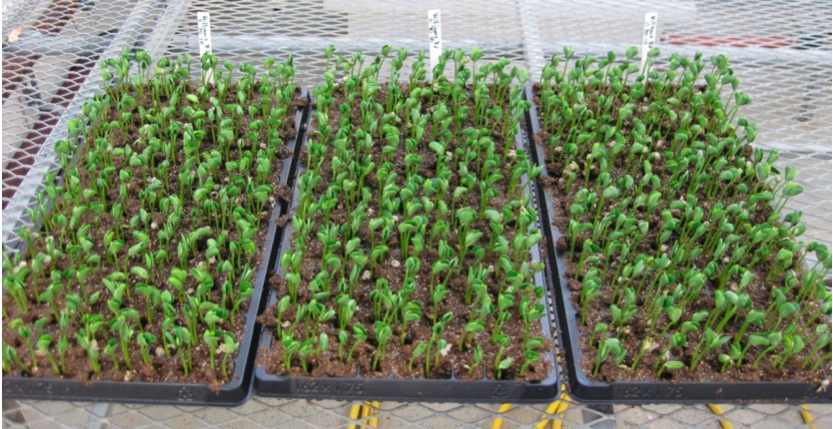
Figure 1. Soybean (William 82) seedlings 7 days after planting
- Count soybean seeds as needed, approximately 162 seeds per DNA construct. Sort the seeds to remove seeds that are diseased, small, or damaged. Remove weed seeds and other extraneous material. The approximate number of soybean cv. Williams 82 seed can be determined by weight using 22.5 grams equals 100 seeds. Seeds from other soybean cultivars may have a different weight per 100 seeds. Sterilize soybean seeds by soaking in 10% bleach for 10 min. 300 ml of 10% bleach in a 1 L plastic beaker works well for up to about 300 grams of seed. Add the seed to the bleach solution, swirl briefly to sink the seeds, and allow the seeds to rest quietly for the remainder of the exposure. Pour off the bleach solution. The seeds were rinsed about 10 times in quick succession with RO [reverse osmosis] water to remove the bleach. Alternatively, run RO water into the beaker until it is full and the seeds are suspended. Continue to run the RO water into the beaker for about 20 sec. Drain the water from the seeds. Repeat 4 times. Drain the seeds well, but gently. Handle the seeds gently, as they are now fragile.
- Prepare the Agrobacterium culture
- Prepare the small Agrobacterium rhizogenes cultures the week before the transformation week.
Inoculate 5 ml of the appropriate culture medium with A. rhizogenes. For cultures of A. rhizogenes strain K599 carrying pRAP15 constructs (Figure 2), the inserts were cloned into the gene expression vector pRAP15 between the attR1 and attR2 sites designed for directional cloning. In this vector, the Figwort Mosaic Virus (FMV) promoter drives expression of the inserted gene. To enable visualization of transformed roots, the vector contains the gene encoding enhanced green fluorescent protein controlled by the rolD promoter that gives strong root expression. A gene encoding tetracycline resistance (TetR) provides antibiotic selection. Inoculate into TB [Terrific Broth] media with 5 μg/ml Tetracycline. Grow two culture tubes of each clone, 5 ml per tube, in the temperature range of 73 F to 74 F [22.8 to 23.3 °C]. The incubation temperature must not rise significantly above 77 F [25 °C] or K599 may expel or modify the plasmids. Shake the tubes at about 200 rpm. Use round bottom 17 x 100 mm 14 ml culture tubes designed for bacteria to avoid clumping of the bacteria. The incubation time will be about 48 to 50 h. - Prepare large cultures of A. rhizogenes.
One or two days before transformation, use the 5 ml cultures to inoculate 300 ml of Terrific Broth (TB) media-5 μg/ml tetracycline for each clone for an overnight incubation at around 73 F to 74 F [22.8 to 23.3 °C]. Inoculate the large culture with one or two of the small cultures depending on culture concentration. The incubation temperature must not rise significantly above 77 F [25 °C] or K599 may expel or modify the plasmid. The 1 L culture flasks are shaken at 160 rpm and 2 L flasks are shaken at 140 rpm for 12 h. Check OD600; they should be in the 0.5 to 0.6 range. The cultures can be stored at 4 °C for 1-2 h until needed.
Note: On the day before transformation, if the lab temperature is expected to be above 75 F [24 °C], turn on the air conditioning to cool both the room and the MS media. The MS media is kept at room temperature or 75 F [24 °C]. Inspect the plantlets to be transformed for disease. Remove plantlets having cotyledons with yellow areas, very tall thin stems, or any other attribute that would make them weak. The plantlets should be dark green with thick, blemish-free cotyledons and thick stems. If the plantlets are not strong enough for the rigors of the transformation, grow the plants again with fresh seed and prepare new bacterial cultures. - Pour the cultures into capped tubes designed for a GSA rotor and balance them. Centrifuge at 5,000 rpm [4,068 x g] at 4 °C for 30 min to collect the A. rhizogenes. (After this point the bacterial cultures do not have to be sterile anymore.)
- Resuspend the pellets in 20 ml MS media. Use a disposable plastic Pasteur pipette to gently resuspend the culture. Transfer about 15ml of the resuspended culture to 190 ml MS. Mix by swirling. Read the OD600. Adjust the culture concentration to about OD600 = 0.5 to 0.6 with MS media.
- Prepare the small Agrobacterium rhizogenes cultures the week before the transformation week.
- Transformation of the base of the soybean seedling with Agrobacterium
- Add 30 ml MS - bacterial solution to 50 ml plastic disposable beakers that will hold the cut plants easily (6 plastic beakers with bacterial solution are needed per construct). With a sharp safety razor blade, excise the seedlings at soil level and immediately place them in beakers containing A. rhizogenes culture. Ensure that the base of the seedling is submerged in the culture. Add about 28 cut plants per beaker. Place the beakers of excised seedlings into a vacuum chamber.
- Apply vacuum 380 mm Hg (Torr) for 30 min to vacuum infiltrate the co-cultivation solution into the plants. Release the vacuum slowly to avoid potential damage to the plants.
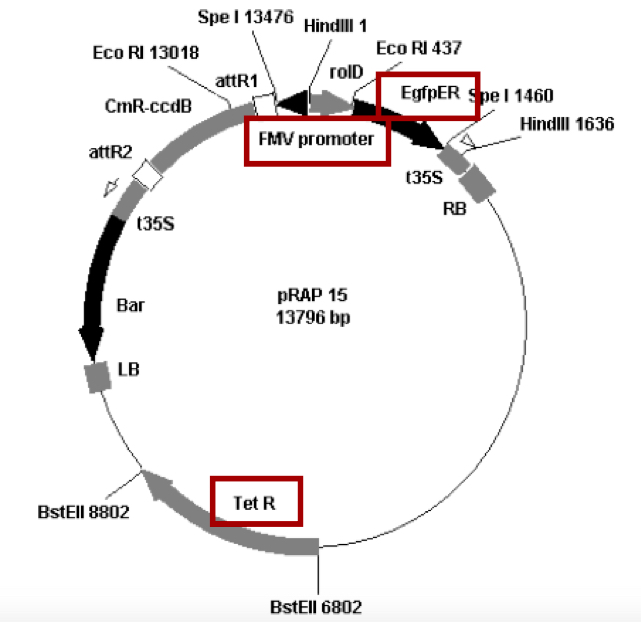
Figure 2. Gateway overexpression vector containing FMV promoter, eGFP and Tet gene pRAP 15 digested with EcoRI(E), HindIII(H), EcoRI/HindIII(E/H) and HindIII/SpeI(H/S) restriction enzymes - Co-cultivate the plants overnight for about 15 h. The plants are placed inside of a clear plastic tub, (Figure 3) which is placed on a rotating platform, moving at 65 rpm. The temperature is held at around 73 F to 74 F [22.8 to 23.3 °C]. The co-cultivation temperature must not rise significantly above 77 F [25 °C] or K599 may expel or modify the plasmids needed for effective transformation.
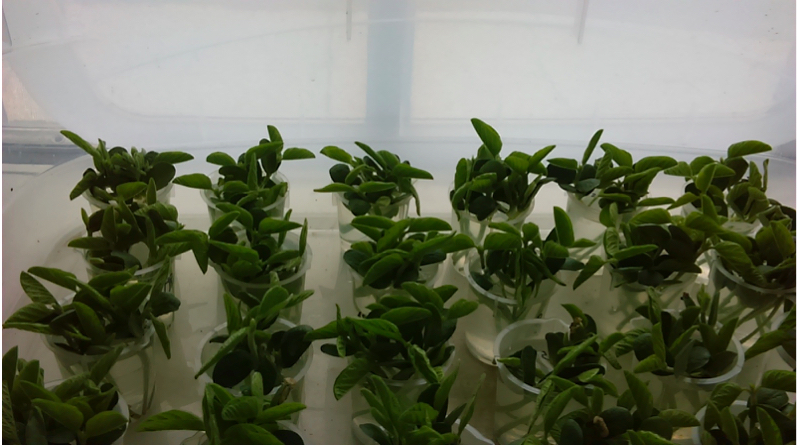

Figure 3. The plantlets are placed inside of a clear plastic tub for co cultivation - Wash the plants with RO water. For each gene, fill two 1 L beakers with RO water up to about 1 cm from the top edge. Remove the plants from one co-cultivation beaker and dip the stem ends about 8x into the first wash beaker and then do the same in the second wash beaker. Place the plants into a clean beaker containing reverse osmosis water. Place the beakers of washed plants in a plastic tub, and store them in the uncovered tub overnight. For each gene, use new, fresh RO water and beakers to avoid cross-contamination. The plants may be stored in the small beakers for up to 4 days after the post co-cultivation wash. All of the wash water should be autoclaved before discarding (Figure 4).

Figure 4. The plantlets are washed with RO water to remove the Agrobacterium
Note: Do not use regular tap water or any water that may contain chlorine, fluorides, or any other water purifying reagent. Fill enough 1 L beakers the night before the post co-cultivation wash to wash all of the plants. This allows RO water to equilibrate to room temperature. Air condition the lab if necessary. - Incubate the plants at about 73 F to 74 F [22.8 to 23.3 °C] under growth lights with a light cycle of about 15 h for about 42 h [two overnights after the post co-cultivation wash] in a growth chamber. The growth lights are about 15 cm from the plants. If the distance is too far, the plants will elongate excessively and possibly jeopardize their health and durability during their recovery in ProMix.
- Add 30 ml MS - bacterial solution to 50 ml plastic disposable beakers that will hold the cut plants easily (6 plastic beakers with bacterial solution are needed per construct). With a sharp safety razor blade, excise the seedlings at soil level and immediately place them in beakers containing A. rhizogenes culture. Ensure that the base of the seedling is submerged in the culture. Add about 28 cut plants per beaker. Place the beakers of excised seedlings into a vacuum chamber.
- Planting the soybean seedlings in the greenhouse
- Before planting the soybean plantlets, pre-wet enough ProMix in a bucket with greenhouse tap water to fill three 32 cell flats fitted within a standard perforated flat per DNA construct. The ProMix should be quite wet; even sodden. Pack the ProMix into the pots with firm hand pressure. Just before planting the plants, sprinkle the ProMix with water from a watering can. Use a marker pen as a dibble to create 2 to 3 cm holes in the ProMix for plant insertion. Insert the plants into the ProMix to about 2 to 3 cm, or close to the cotyledons, and lightly compress the ProMix down with four fingers encircling the stem. After planting the plants, thoroughly sprinkle the ProMix with water from a watering can. The planting day is day 0.
Note: Do not use ProMix with Biofungicide. It may interfere with assays of roots involving nematodes and fungi. - Water the plants gently with a watering can for the first 4 days after planting in ProMix. Switch to watering with a wand on day 5. Water with plain water for the first 9 days after planting in ProMix. On day 10, begin feeding the plants 3 days with a Spot Sprayer or watering can and 1x Peters Excel 13-2-13 150 ppm nitrogen (pH 6.1).
- If restricted shoot growth is desired, the top of the plants above the 2nd trifoliate (on about day 15) may be cut off. Use stainless steel scissors that have been cleaned with alcohol or anti-bacterial soap. This time period will vary with the season and growing conditions. During the summer months, two toppings may be necessary. Plants were grown in a greenhouse under natural light supplemented daily with a 12 h:12 h light: dark cycle of artificial light. Greenhouse temperatures were maintained at 25 °C (days) and 14 °C (nights) with 20-50% humidity.
- Before planting the soybean plantlets, pre-wet enough ProMix in a bucket with greenhouse tap water to fill three 32 cell flats fitted within a standard perforated flat per DNA construct. The ProMix should be quite wet; even sodden. Pack the ProMix into the pots with firm hand pressure. Just before planting the plants, sprinkle the ProMix with water from a watering can. Use a marker pen as a dibble to create 2 to 3 cm holes in the ProMix for plant insertion. Insert the plants into the ProMix to about 2 to 3 cm, or close to the cotyledons, and lightly compress the ProMix down with four fingers encircling the stem. After planting the plants, thoroughly sprinkle the ProMix with water from a watering can. The planting day is day 0.
- Evaluate the transformation by checking the soybean roots and trimming the untransformed roots
- On about day 38, (Figure 5) gently remove the soil from all plants in each clone group by placing them in a 4 gallon autoclavable bucket. Gently massage the root mass to remove Promix. Rinse the roots with room temperature water. One bucket can be used to wash about 50 plants. Store the de-soiled plants in a 2 gallon bucket containing 0.5x Peters Excel 13-2-13 75 ppm nitrogen (pH 6.1).
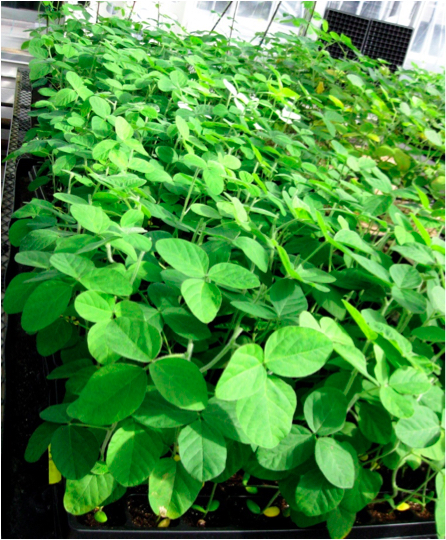

Figure 5. Soybean plants are in the greenhouse and growing well 38 days after transformation - In a dark room, use the Dark Reader Spot Lamp-SL85 and orange filter glasses to visualize the GFP roots (Figure 6). Discard plants with no GFP roots. Identify 20 or more of the best composite plants with good GFP roots for the experiment. The transformation efficiency ranges from 65 to 90%.
- With scissors, cut off the non-GFP roots on the composite plants. Maintain the composite plants in the greenhouse with their roots submerged in 0.5x Peters Excel 13-2-13 at about 75 ppm nitrogen (pH 6.1) for two nights in order to minimize wilting after they are replanted in sand.
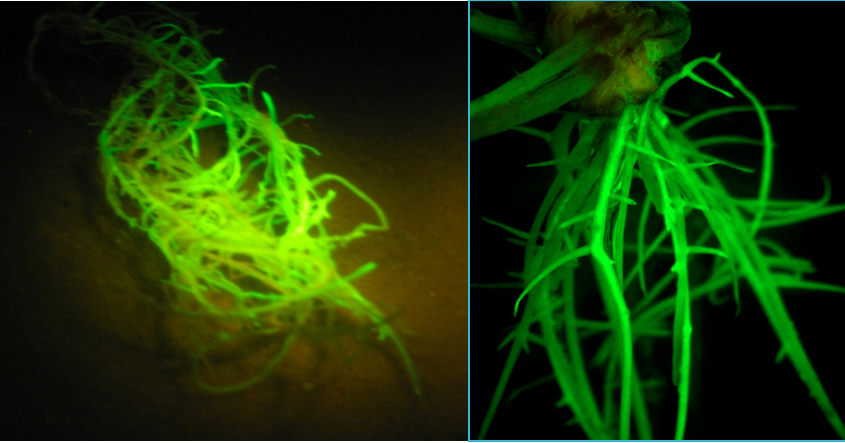
Figure 6. Soybean roots exposed to Dark Light® to visualize GFP-expressing roots - Plant the composite plants in flooded, sterile sand to help them recover from the removal of non-GFP roots. Place 2 cm of sand in each cell. Place the root of the plant in the cell, with the base of the seedling 1 cm below the top of the cell. Gently sprinkle wet sand around and on top of the roots. Build a compact cone of sand 2 to 3 cm tall around the base of the seedling to hold it upright. Place the cell in a flat. Flood the flat with 0.5x Peters Excel 13-2-13 75 ppm nitrogen. Leave the plants in flooded sand for 2 days.
- Transfer the plants to perforated flats containing wet Promix about 2.5 cm deep. Allow the plants to drain overnight.
- The next day, inoculate with nematodes.
Note: If the plantlets appear wilted after the non-GFP roots are excised, put them in the shade to protect them from direct sunlight until they have recovered.
- On about day 38, (Figure 5) gently remove the soil from all plants in each clone group by placing them in a 4 gallon autoclavable bucket. Gently massage the root mass to remove Promix. Rinse the roots with room temperature water. One bucket can be used to wash about 50 plants. Store the de-soiled plants in a 2 gallon bucket containing 0.5x Peters Excel 13-2-13 75 ppm nitrogen (pH 6.1).
Recipes
- MS media
Adjust the pH to 5.7Preparation 1 L MS salts 4.4 g 3% sucrose 30 g
If the MS media is to be used within a day, there is no need to autoclave. - Terrific Broth, Modified
RPI Premixed Terrific Broth
No need to pH the mediaContents of the Terrific Broth premix 1 L Casein digest peptone 12 g/L Yeast extract 24 g/L Dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4) 9.4 g/L Potassium phosphate (K3PO4) 2.2 g/L Preparation 1 L Add TB premix to 1 L water 47.6 g Glycerol 4 ml
Autoclave 20 min - Scotts Peters Excel 13-2-13 16x Fertilizer
Prepare 1 gallon of water with 13 pellets KOH
Mix each solution well
Prepare 1 gallon of water with 10 tablespoons [10T] Peters Excel13-2-13, Scotts Peters Excel 13-2-13 32x
Mix Combine the two solutions and mix well separately
pH 6.2
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from our previous work, including (Matthews et al., 2013; 2014 and Youssef et al., 2013). We thank Hunter Beard for technical support. Mention of trade name, proprietary product or vendor does not constitute a guarantee or warranty of the product by the U. S. Department of Agriculture or imply its approval to the exclusion of other products or vendors that also may be suitable. The authors have no conflict of interest.
References
- Matthews, B. F., Beard, H., Brewer, E., Kabir, S., MacDonald, M. H. and Youssef, R. M. (2014). Arabidopsis genes, AtNPR1, AtTGA2 and AtPR-5, confer partial resistance to soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines) when overexpressed in transgenic soybean roots. BMC Plant Biol 14: 96.
- Matthews, B. F., Beard, H., MacDonald, M. H., Kabir, S., Youssef, R. M., Hosseini, P. and Brewer, E. (2013). Engineered resistance and hypersusceptibility through functional metabolic studies of 100 genes in soybean to its major pathogen, the soybean cyst nematode. Planta 237(5): 1337-1357.
- Youssef, R. M., MacDonald, M. H., Brewer, E. P., Bauchan, G. R., Kim, K. H. and Matthews, B. F. (2013). Ectopic expression of AtPAD4 broadens resistance of soybean to soybean cyst and root-knot nematodes. BMC Plant Biol 13: 67.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Matthews, B. F. and Youssef, R. M. (2016). Agrobacterium rhizogenes-Based Transformation of Soybean Roots to Form Composite Plants. Bio-protocol 6(2): e1708. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1708.
Category
Plant Science > Plant developmental biology > General
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > DNA
Plant Science > Plant transformation > Agrobacterium
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link