- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Flow Cytometric Analysis of Drug-induced HIV-1 Transcriptional Activity in A2 and A72 J-Lat Cell Lines
Published: Vol 7, Iss 10, May 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2290 Views: 10345
Reviewed by: Emilie BesnardEmilie BattivelliAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Single-cell Damagenome Profiling by Linear Copying and Splitting based Whole Genome Amplification (LCS-WGA)
Yichi Niu [...] Chenghang Zong
Mar 20, 2022 1510 Views
A Mouse Infection Model with a Wildtype Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Strain for the Analysis of Inflammatory Innate Immune Cells
Christa Pfeifhofer-Obermair [...] Günter Weiss
Apr 5, 2022 1238 Views
Isolation of Epithelial and Stromal Cells from Colon Tissues in Homeostasis and Under Inflammatory Conditions
Clara Morral [...] Kathryn E. Hamilton
Sep 20, 2023 963 Views
Abstract
The main obstacle to eradicating HIV-1 from patients is post-integration latency (Finzi et al., 1999). Antiretroviral treatments target only actively replicating virus, while latent infections that have low or no transcriptional activity remain untreated (Sedaghat et al., 2007). A combination of antiretroviral treatments with latency-purging strategies may accelerate the depletion of latent reservoirs and lead to a cure (Geeraert et al., 2008). Current strategies to reactivate HIV-1 from latency include use of prostratin, a non-tumor-promoting phorbol ester (Williams et al., 2004), BET inhibitors (Filippakopoulos et al., 2010; Delmore et al., 2011), and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, such as suberoylanilidehydroxamic acid (i.e., SAHA or Vorinostat) (Kelly et al., 2003; Archin et al., 2009; Contreras et al., 2009; Edelstein et al., 2009). As the mechanisms of HIV-1 latency are diverse, effective reactivation may require combinatorial strategies (Quivy et al., 2002). The following protocol describes a flow cytometry-based method to quantify transcriptional activation of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat (LTR) upon drug treatment. This protocol is optimized for studying latently HIV-1-infected Jurkat (J-Lat) cell lines that contain a GFP cassette. J-Lats that contain a different reporter, for example Luciferase, can be treated with drugs as described but have to be analyzed differently.
Keywords: Human immunodeficiency virus-1Background
Studies that assess transcriptional activation or repression of the HIV-1 LTR generally use CD4+ T cells containing latent full-length HIV-1, such as NL4-3/E-/GFP-IRES–nef (Kutsch et al., 2002) or R7/E-/GFP (Jordan et al., 2003), which contains a frameshift mutation in the viral Env gene to prevent viral spread and expresses GFP in the Nef open reading frame allowing separation of actively infected GFP+ from GFP− cells (uninfected or latently infected) by cell sorting (Jordan et al., 2003). To specifically investigate transcriptional activation of the HIV-1 LTR, we utilize the J-Lat cell line A72 containing only a latent LTR-GFP construct (Jordan et al., 2003). To determine if drug treatment specifically activates Tat, we utilize a J-Lat cell line harboring a latent lentiviral construct expressing Tat with GFP from the HIV-1 LTR (clone A2; LTR-Tat-IRES-GFP) (Jordan et al., 2003).
Materials and Reagents
- A2 and A72 J-Lat cell culture
- 75 cm2 tissue culture flask (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 353110 )
- Tips
0.1-10 µl (Fisher Scientific, FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 02-681-440 )
1-200 µl (Fisher Scientific, FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 02-707-502 )
101-1,000 µl (Fisher Scientific, FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 02-707-509 ) - A2 and A72 J-Lat cells (Jordan et al., 2003)
- RPMI (Mediatech, catalog number: 10-040-CV )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gemini Bio-Products, catalog number: 100-106 )
- L-glutamine (Mediatech, catalog number: 25-005-Cl )
- 100x penicillin/streptomycin (Mediatech, catalog number: 30-002-Cl )
- 75 cm2 tissue culture flask (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 353110 )
- Analysis of HIV-1 LTR transcriptional activation by flow cytometry
- 96-well V-bottom tissue culture plates and lids (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo Scientific TM, catalog numbers: N249570 and N163320 )
- Tips
0.1-10 µl (Fisher Scientific, FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 02-681-440 )
1-200 µl (Fisher Scientific, FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 02-707-502 )
101-1,000 µl (Fisher Scientific, FisherbrandTM, catalog number: 02-707-509 ) - RPMI (Mediatech, catalog number: 10-040-CV )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gemini Bio-Products, catalog number: 100-106 )
- L-glutamine (Mediatech, catalog number: 25-005-Cl )
- 100x penicillin/streptomycin (Mediatech, catalog number: 30-002-Cl )
- TNFα (PeproTech, catalog number: 300-01A )
- JQ1 (Cayman Chemical, catalog number: 11187 )
- Prostratin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P0077 )
- Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: SML0061 )
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8418 )
- 1x PBS (Mediatech, catalog number: 21-031-CV )
- MACSQuant Running buffer (Miltenyi Biotech, catalog number: 130-092-747 )
- ApoTox-GloTM Triplex Assay (Promega, catalog number: G6320 )
- RPMI medium (see Recipes)
- TNFα stock solution (see Recipes)
- JQ1 stock solution (see Recipes)
- Prostratin stock solution (see Recipes)
- Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) stock solution (see Recipes)
- 96-well V-bottom tissue culture plates and lids (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo Scientific TM, catalog numbers: N249570 and N163320 )
Equipment
- Pipette
- Biosafety cabinet level 2
- CO2 tissue culture incubator (Thermo Electron, model: FormaTM Steri-CultTM CO2 Incubators , catalog number: 3307)
- Tabletop centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Allegra X-14R ) for 96-well plates
- MACSQuant VYB FACS analyzer (Miltenyi Biotech, model: MACSOuant® VYB, catalog number: 130-096-116 )
- SpectraMax MiniMaxTM 300 Imaging Cytometer (Molecular Devices, model: SpectraMax MiniMax 300 )
Software
- FlowJo 9.9 or never (Tree Star)
Procedure
- A2 and A72 J-Lat suspension cell culture
- A2 and A72 cells are cultured in RPMI medium (supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% L-glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin) in 75 cm2 tissue culture flasks in 40 ml medium. The flasks are placed horizontally to increase the surface area in which the cells are grown.
- Cells are split every 1-2 days and should be kept at a concentration of 2 x 105/ml-1.5 x 106/ml.
- One day before drug treatment split A2 or A72 cells to 5 x 105/ml.
- A2 and A72 cells are cultured in RPMI medium (supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% L-glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin) in 75 cm2 tissue culture flasks in 40 ml medium. The flasks are placed horizontally to increase the surface area in which the cells are grown.
- Analysis of HIV-1 LTR transcriptional activation by flow cytometry
- Count the cells and adjust cell number with new media. About 2 x 105/well of A2 or A72 cells are plated in 96-well tissue culture plates in 195 µl RPMI medium (supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% L-glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin). For each condition perform three replicates.
- Cells are stimulated with 0.016-10 ng/ml of TNFα, 100 nM-1 µM JQ1, 100 nM-2.5 µM Prostratin, 330 nM-2.5 µM SAHA, DMSO control, or left untreated. If treated with TNFα, use PBS or water as control, depending on what was used as diluent. All drugs and controls are pipetted in 5 µl to reach a total volume of 200 µl/well. Mix cells and drugs by pipetting up and down at least 3 times.
- Culture in a CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 18-48 h.
- Take the plate from the incubator and centrifuge at room temperature for 2 min at 1341 x g (2,400 rpm) (Tabletop centrifuge, Beckman).
- Then proceed directly to flow cytometry analysis. Cells do not have to be washed or fixed.
Notes: - For flow cytometry, MACSQuant VYB FACS analyzer was used to run 96-well plates. However, other flow cytometers such as Calibur or LSRII are also suitable for these experiments.
- If the analysis of cell viability by forward scatter (FSC) vs. side scatter (SSC) is not sufficient for accurate assessment of drug toxicity in drug studies, one of a variety of dyes/stains; for example 7AAD, Propidium iodide or one of the Zombie viability dyes can be used according to manufacturer’s instructions in the flow cytometric analysis in this protocol.
- Viability, cytotoxicity and apoptosis was measured with ApoTox-GloTM Triplex Assay (Promega) according to manufacturer’s instructions using a SpectraMax MiniMaxTM 300 Imaging Cytometer (Figure 1).
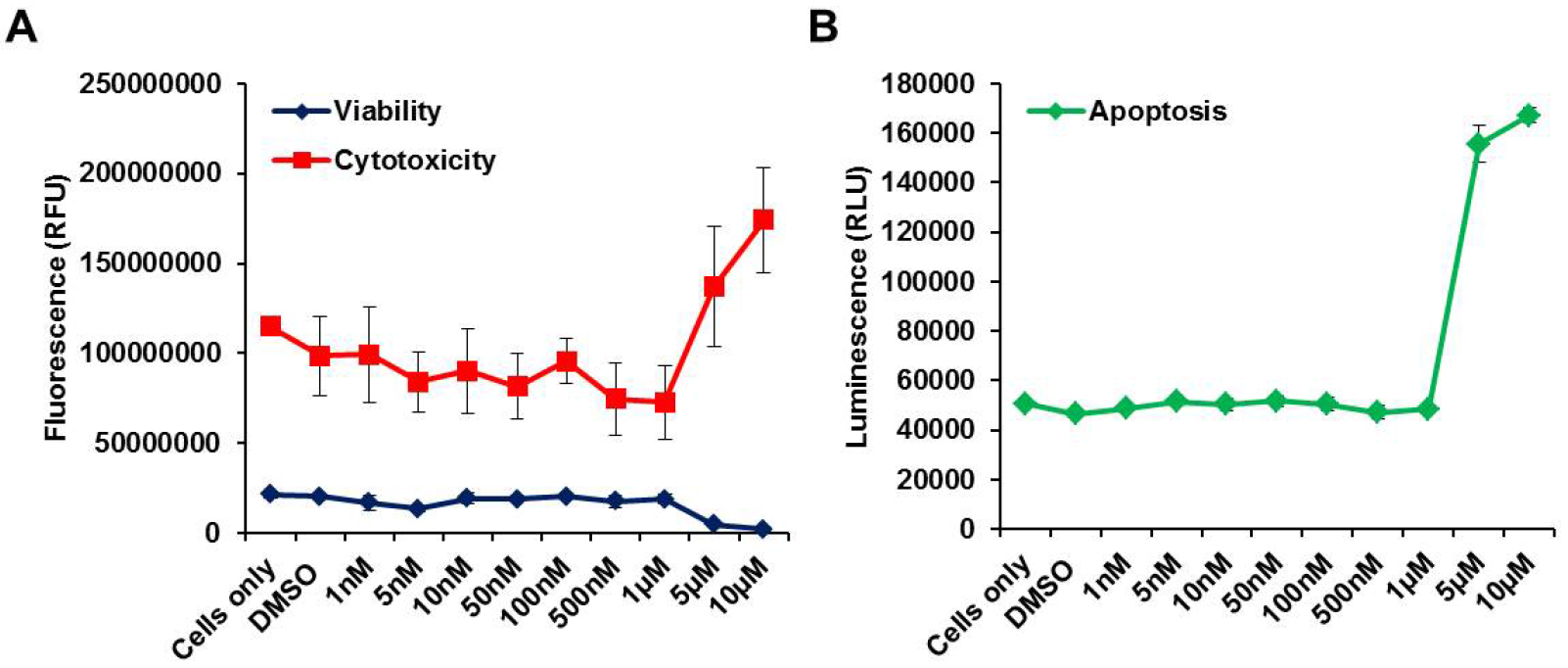
Figure 1. Measurement of Viability, Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis of drug treated cells. ApoTox-GloTM Triplex Assays (Promega) were performed in drug-treated A72 J-Lat cells. A. Cytotoxicity and Viability; B. Apoptosis; All measurements were repeated at least three times and average of three technical replicates (± SD) is shown.
- Count the cells and adjust cell number with new media. About 2 x 105/well of A2 or A72 cells are plated in 96-well tissue culture plates in 195 µl RPMI medium (supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% L-glutamine and 1% penicillin/streptomycin). For each condition perform three replicates.
Data analysis
Analysis of HIV-1 LTR transcriptional activation by flow cytometry (Figure 2)
- First, set the gate on live J-Lat cells. Cell viability is monitored by forward (FSC-Area) and side scatter (SSC-Area) analysis (Figure 2A).
- Gate on singlets (FSC-Height vs. FSC-Area) (Figure 2B).
- Set the gate on SSC-Area and GFP/FITC-Area to identify the amount of GFP+ cells (Figure 2C).
- Each sample is usually analyzed in triplicate and the experiment is performed with cells coming from at least 3 independent experiments (Figure 3). Three replicates are averaged by calculating (GFP+ cells Experiment 1 + GFP+ cells Experiment 2 + GFP+ cells Experiment 3)/3. Also calculate standard deviation (STDEV) for error bars.
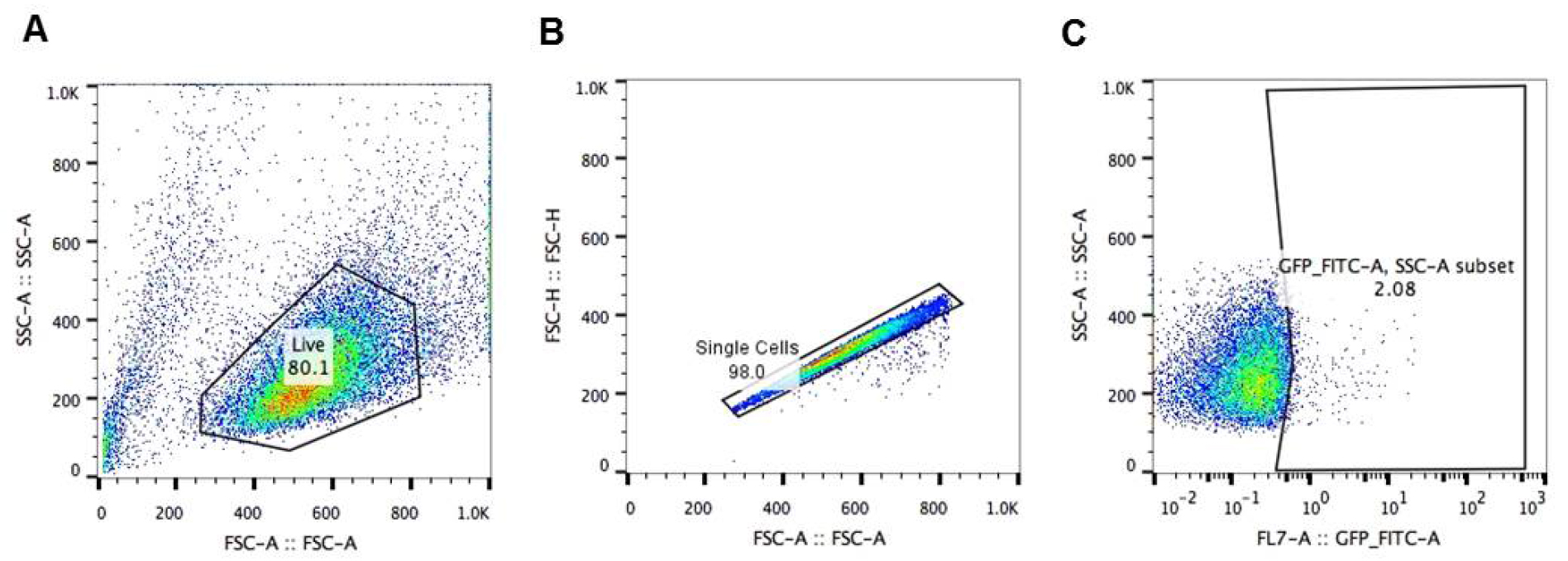
Figure 2. Analysis of HIV-1 LTR transcriptional activation by flow cytometry. Gating strategy to analyze A2 or A72 J-Lat cells: A. gating on live J-Lat cells based on size (FSC-Area) and granularity (SSC-Area); B. singlets gate (FSC-Height vs. FSC-Area); C. gating on GFP+ J-Lat cells (SSC-Area vs. GFP-FITC-Area).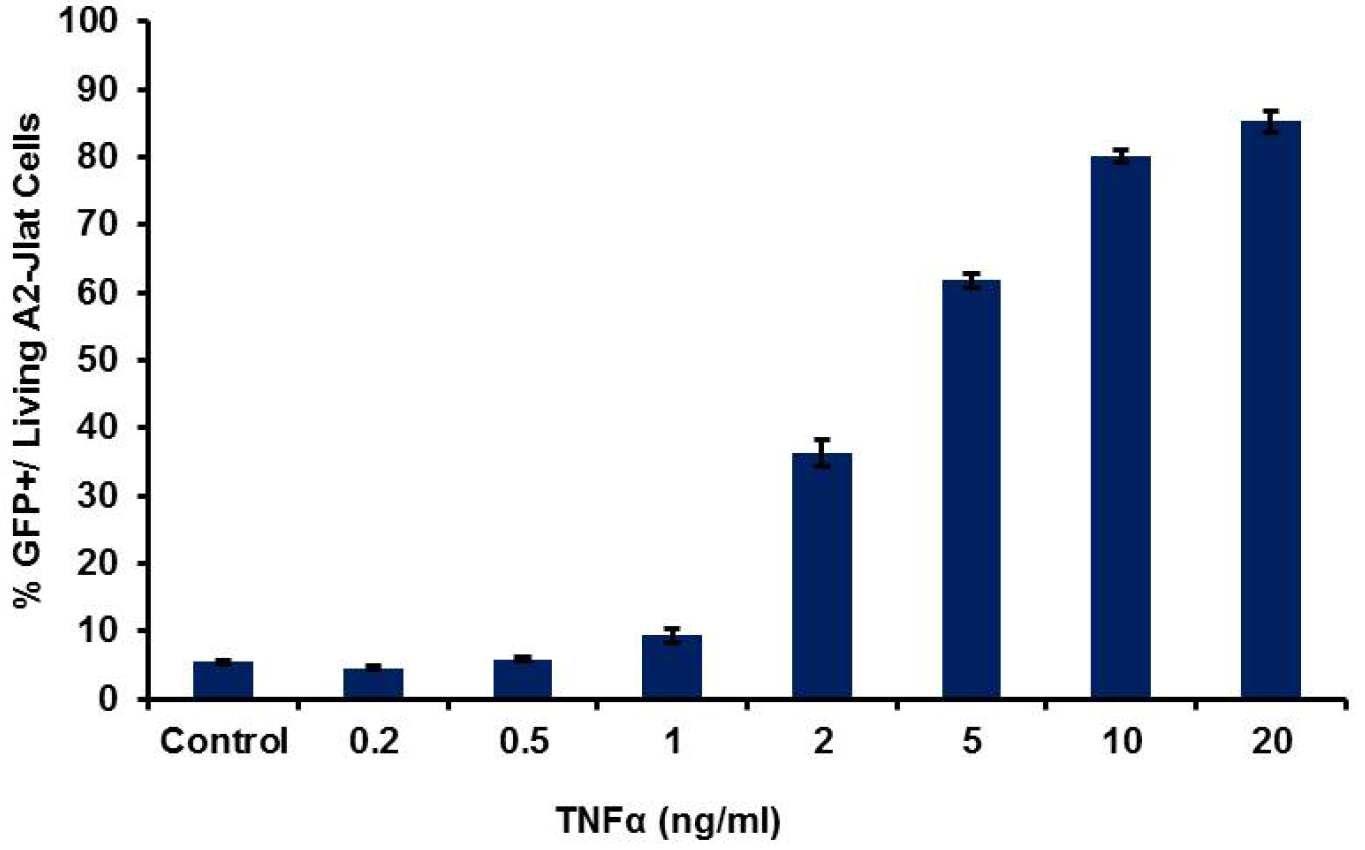
Figure 3. HIV-1 LTR transcriptional activation by flow cytometry. Typical results obtained for 18 h treatment with TNFα, with dose dependent response using A2 J-Lat cells. Average for percentage of GFP+ cells from three replicates (± SD) is shown.
Recipes
- RPMI medium
RPMI supplemented with,
10% FBS
1% L-glutamine
1% penicillin/streptomycin
Store at 4 °C - TNFα stock solution
100 ng/μl in sterile water
Store at -80 °C - JQ1 stock solution
10 mM in DMSO
Store at -80 °C
Note: Avoid repeated freeze-thaws! - Prostratin stock solution
5 mM in sterile water
Store at -20 °C - Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) stock solution
10 mM in DMSO
Store at -20 °C
Acknowledgments
We thank Marielle Cavrois and the Flow cytometry core for the service provided for flow cytometry. This publication was made possible with the help from the University of California, San Francisco–Gladstone Institute of Virology & Immunology Center for AIDS Research (CFAR), an NIH-funded program (P30 AI027763). This research was supported as part of the amfAR Institute for HIV Cure Research, with funding from amfAR grant number 109301. Further, we gratefully acknowledge support from the California HIV/AIDS Research Program (Award number: F13-GI-316) to D.B., and grant support from the CARE Collaboratory (U19 AI096113) and the NIH (RO1 AI083139 and RO1 DA043142) to M.O. This protocol was adapted from previous work: ‘BET bromodomain-targeting compounds reactivate HIV from latency via a Tat-independent mechanism’ (Boehm et al., 2013).
References
- Archin, N. M., Espeseth, A., Parker, D., Cheema, M., Hazuda, D. and Margolis, D. M. (2009). Expression of latent HIV induced by the potent HDAC inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 25(2): 207-212.
- Boehm, D., Calvanese, V., Dar, R. D., Xing, S., Schroeder, S., Martins, L., Aull, K., Li, P. C., Planelles, V., Bradner, J. E., Zhou, M. M., Siliciano, R. F., Weinberger, L., Verdin, E. and Ott, M. (2013). BET bromodomain-targeting compounds reactivate HIV from latency via a Tat-independent mechanism. Cell Cycle 12(3): 452-462.
- Contreras, X., Schweneker, M., Chen, C. S., McCune, J. M., Deeks, S. G., Martin, J. and Peterlin, B. M. (2009). Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid reactivates HIV from latently infected cells. J Biol Chem 284(11): 6782-6789.
- Delmore, J. E., Issa, G. C., Lemieux, M. E., Rahl, P. B., Shi, J., Jacobs, H. M., Kastritis, E., Gilpatrick, T., Paranal, R. M., Qi, J., Chesi, M., Schinzel, A. C., McKeown, M. R., Heffernan, T. P., Vakoc, C. R., Bergsagel, P. L., Ghobrial, I. M., Richardson, P. G., Young, R. A., Hahn, W. C., Anderson, K. C., Kung, A. L., Bradner, J. E. and Mitsiades, C. S. (2011). BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell 146(6): 904-917.
- Edelstein, L. C., Micheva-Viteva, S., Phelan, B. D. and Dougherty, J. P. (2009). Short communication: activation of latent HIV type 1 gene expression by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), an HDAC inhibitor approved for use to treat cutaneous T cell lymphoma. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 25(9): 883-887.
- Filippakopoulos, P., Qi, J., Picaud, S., Shen, Y., Smith, W. B., Fedorov, O., Morse, E. M., Keates, T., Hickman, T. T., Felletar, I., Philpott, M., Munro, S., McKeown, M. R., Wang, Y., Christie, A. L., West, N., Cameron, M. J., Schwartz, B., Heightman, T. D., La Thangue, N., French, C. A., Wiest, O., Kung, A. L., Knapp, S. and Bradner, J. E. (2010). Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 468(7327): 1067-1073.
- Finzi, D., Blankson, J., Siliciano, J. D., Margolick, J. B., Chadwick, K., Pierson, T., Smith, K., Lisziewicz, J., Lori, F., Flexner, C., Quinn, T. C., Chaisson, R. E., Rosenberg, E., Walker, B., Gange, S., Gallant, J. and Siliciano, R. F. (1999). Latent infection of CD4+ T cells provides a mechanism for lifelong persistence of HIV-1, even in patients on effective combination therapy. Nat Med 5(5): 512-517.
- Geeraert, L., Kraus, G. and Pomerantz, R. J. (2008). Hide-and-seek: the challenge of viral persistence in HIV-1 infection. Annu Rev Med 59: 487-501.
- Jordan, A., Bisgrove, D. and Verdin, E. (2003). HIV reproducibly establishes a latent infection after acute infection of T cells in vitro. EMBO J 22(8): 1868-1877.
- Kelly, W. K., Richon, V. M., O'Connor, O., Curley, T., MacGregor-Curtelli, B., Tong, W., Klang, M., Schwartz, L., Richardson, S., Rosa, E., Drobnjak, M., Cordon-Cordo, C., Chiao, J. H., Rifkind, R., Marks, P. A. and Scher, H. (2003). Phase I clinical trial of histone deacetylase inhibitor: suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid administered intravenously. Clin Cancer Res 9(10 Pt 1): 3578-3588.
- Kutsch, O., Benveniste, E. N., Shaw, G. M. and Levy, D. N. (2002). Direct and quantitative single-cell analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reactivation from latency. J Virol 76(17): 8776-8786.
- Quivy, V., Adam, E., Collette, Y., Demonte, D., Chariot, A., Vanhulle, C., Berkhout, B., Castellano, R., de Launoit, Y., Burny, A., Piette, J., Bours, V. and Van Lint, C. (2002). Synergistic activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter activity by NF-kappaB and inhibitors of deacetylases: potential perspectives for the development of therapeutic strategies. J Virol 76(21): 11091-11103.
- Sedaghat, A. R., Siliciano, J. D., Brennan, T. P., Wilke, C. O. and Siliciano, R. F. (2007). Limits on replenishment of the resting CD4+ T cell reservoir for HIV in patients on HAART. PLoS Pathog 3(8): e122.
- Williams, S. A., Chen, L. F., Kwon, H., Fenard, D., Bisgrove, D., Verdin, E. and Greene, W. C. (2004). Prostratin antagonizes HIV latency by activating NF-κB. J Biol Chem 279(40): 42008-42017.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Boehm, D. and Ott, M. (2017). Flow Cytometric Analysis of Drug-induced HIV-1 Transcriptional Activity in A2 and A72 J-Lat Cell Lines. Bio-protocol 7(10): e2290. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2290.
Category
Cell Biology > Single cell analysis > Flow cytometry
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link