- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Thermal Stability of Heterotrimeric pMHC Proteins as Determined by Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
Published: Vol 7, Iss 13, Jul 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2366 Views: 8186
Reviewed by: Jia LiAna Santos AlmeidaPalash Kanti DuttaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Protocol to Isolate Germinal Centers by Laser Microdissection
Farbod Bahreini [...] Kathrin Kalies
Jun 5, 2022 1179 Views
Immunohistochemistry of Immune Cells and Cells Bound to in vivo Administered Antibodies in Liver, Lung, Pancreas, and Colon of B6/lpr Mice
Kieran Adam and Adam Mor
Jul 20, 2022 1819 Views
High-throughput Assessment of Mitochondrial Protein Synthesis in Mammalian Cells Using Mito-FUNCAT FACS
Hironori Saito [...] Shintaro Iwasaki
Feb 5, 2023 418 Views
Abstract
T cell receptor (TCR) recognition of foreign peptide fragments, presented by peptide major histocompatibility complex (pMHC), governs T-cell mediated protection against pathogens and cancer. Many factors govern T-cell sensitivity, including the affinity of the TCR-pMHC interaction and the stability of pMHC on the surface of antigen presenting cells. These factors are particularly relevant for the peptide vaccination field, in which more stable pMHC interactions could enable more effective protection against disease. Here, we discuss a method for the determination of pMHC stability that we have used to investigate HIV immune escape, T-cell sensitivity to cancer antigens and mechanisms leading to autoimmunity.
Keywords: Peptide-MHC stabilityBackground
The ability of CD8+ T-cells to respond to foreign invaders or dysregulated self is dependent on stable pMHC class I (pMHCI) presentation at the cell surface. Structurally, MHCI molecules form a peptide binding groove formed of two parallel α helices with a floor of β sheets at the interface between the α1 and α2 domains (Latron et al., 1992). The peptide binding groove has primary peptide binding pockets (B and F) that tightly interact with specific amino acids towards the N- and C-terminals of bound peptides. Although these pockets can accommodate a range of amino acids, they exhibit preferences for certain side chains that have been characterized using structural and biochemical approaches (Parker et al., 1992). This information has been used to generate so called ‘heteroclitic’ peptides in which natural peptides that have poor MHC-anchors can be modified with amino acids that bind optimally to MHC for vaccination (Cole et al., 2010). Moreover, pMHC stability has been linked to HIV immune escape (Bronke et al., 2013) and the selection of autoreactive T-cell clones (Yin et al., 2011). Thus, understanding the mechanisms that control pMHC stability is important for therapeutic design and understanding complex human diseases. Here, we developed a protocol to accurately determine pMHC stability using circular dichroism spectroscopy. We have used this technique, together with structural, biophysical and cellular experiments, to provide new insight into the molecular factors that determined T-cell antigen recognition in the context of a range of human diseases (Kløverpris et al., 2015; Knight et al., 2015; Motozono et al., 2015; Cole et al., 2016; Jones et al., 2016; Cole et al., 2017).
Materials and Reagents
- Cellulose nitrate 0.45 µm filter papers (Sartorius, catalog number: 11306-47-N )
- 1.2 µm glass microfiber filters (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 1822-070 )
- 10 ml plastic syringes, Luer slip BD Plastipak (BD, catalog number: 302188 )
- 25 G needle (BD, catalog number: 300600 )
- 1 ml plastic syringes, Luer slip BD Plastipak (BD, catalog number: 303172 )
- 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes
- Amicon centrifugal concentrating tubes 4 ml MWCO 10 kDa (Merck, catalog number: UFC801096 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) made up from Dulbecco A tablets (137 mM NaCl, 3 mM KCl, 8 mM Na2HPO4, 1.5 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.3) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: BR0014G )
- Ultrapure water (> 18 MΩ cm) for buffer preparations
- Bolt® Bis-Tris 4-12% precast gels (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: NW04120BOX )
- BlUeye prestained protein markers (Geneflow, catalog number: S6-0024 )
- Quick Coomassie Stain (Generon, catalog number: GEN-QC-STAIN-3L )
- Ethanol absolute (200 Proof)
- Nitric acid (HNO3), 70%
Equipment
- Reusable bottle top filtration device (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: DS0320-5045 )
- Vacuum pump such as KNF Neuberger Vaccum Pump (KNF Neuberger, catalog number: 049268/018121 )
- 500 ml clear Duran bottles (Duran, catalog number: GL 45 )
- Liquid Chromatography system, with a 2 ml injection loop, and a fraction collector; we use the ÄKTA pure 25 L with an F9-R fraction collector (GE Healthcare, model: ÄKTA pure 25 L )
- Size exclusion chromatography column; we use a Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 GL column, bed volume 24 ml (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 28990944 )
- Benchtop refrigerated micro-centrifuge capable of 14,000 x g (e.g., Eppendorf, model: 5418 R )
- Far-UV spectrophotometer with a bandwidth < 1.8 nm and quartz cuvettes. We use a single-beam Beckman DU 800 instrument with microcells that allow measurements with volumes of 50 to 100 μl (Beckman Coulter, model: DU® 800 )
- A far-UV circular dichroism (CD) spectrometer with a temperature controlled cell holder. We use an AVIV Model 215 instrument (Aviv Biomedical, model: Aviv Model 215 ) with a single cell Peltier controlled cell holder, or make use of the Module B end-station spectrophotometer at the B23 Synchrotron Radiation CD (Diamond Light Source, model: B23 ) Beamline at the Diamond Light Source (Jávorfi et al., 2010; Cole et al., 2016). Alternative instruments are available from Applied Photophysics Ltd (Leatherhead, U.K.), JASCO Inc. (Easton, MD), and Olis Inc. (Bogart, GA)
- Strain free sealable quartz cuvettes of appropriate path length fitting the CD instrument’s cell holder. We use Teflon stoppered Hellma Suprasil cells of various thickness, mostly 0.1-cm
- A well-ventilated chemical fume hood should be accessible for cleaning cuvettes with HNO3
Software
- An analysis software that can import the CD data files and allows curve fitting to a user defined set of equations is required. We use Origin version 7.5 and later (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA), but many other programs. e.g., Igor Pro, MATLAB, Micromath Scientist, SigmaPlot, etc. will work
Procedure
- Purification and buffer exchange of pMHC protein
HLA-A2 and human β2-microglobulin (β2m) sequences were generated as described and cloned into separate pGMT7 expression plasmids (Cole et al., 2007). Complexes of HLA-A2, β2m and peptides are refolded and purified as described (Bulek et al., 2012, MacLachlan et al., 2017) with the essential steps summarized below. For CD analysis, proteins should be of high purity and the preparation should lack the presence of denatured or incorrectly folded protein. In order to achieve this, the proteins are purified on the day of, or the day before analysis, and stored on ice to avoid any freeze thaw cycles.- Prepare a 500 ml solution of PBS using 1 tablet per 100 ml of ultra-pure water. With the bottle top filtration device and vacuum pump, filter this solution through a cellulose nitrate 0.45 µm filter paper, with a 1.2 µm glass microfiber filter as a pre-filter, into a 500 ml Duran bottle. Prepare another 500 ml Duran bottle of ultra-pure water.
- Connect the gel filtration column to the ÄKTA FPLC system and wash with sterile ultra-pure water followed by equilibrating the system with PBS. Wash the 2 ml injection loop with ultra-pure water and equilibrate with PBS using a 10 ml syringe, taking special care to avoid the occurrence of any air gaps that can be transferred to the column.
- Using a 25 G needle transfer the protein solution, of no more than 1 ml, into the injection loop using a 1 ml syringe avoiding any air bubbles.
- Run the column at 0.5 ml/min and monitor elution by UV absorbance at 280 nm (Note 1). Collect 1-ml fractions (the number of fractions depends on the elution profile, but we try and take 2-4 fractions from the center of the peak) and analyse by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions to check for purity of the pMHC sample. We use 4-12% gradient Bolt® Bis-Tris gels, BLUeye prestained protein ladder, NuPAGE MES running buffer, and Quick Coomassie Stain.
- Run an SDS-PAGE. Upon SDS-PAGE, pMHC dissociates into its constituent parts. Bands of HLA-A2 and β2m run at positions corresponding to ~32 and ~12 kDa, respectively. The peptide (~1 kDa) will run out of the gel (Figure 1).
- Combine only the purest two or three fractions and concentrate using an Amicon centrifugal filtration tube with an MWCO of 10 kDa. This provides protein of adequate purity and concentration for CD analysis.
- Directly before CD measurements, spin the samples at 14,000 x g for 20 min at 4 °C usually without resulting in any visible pellet.
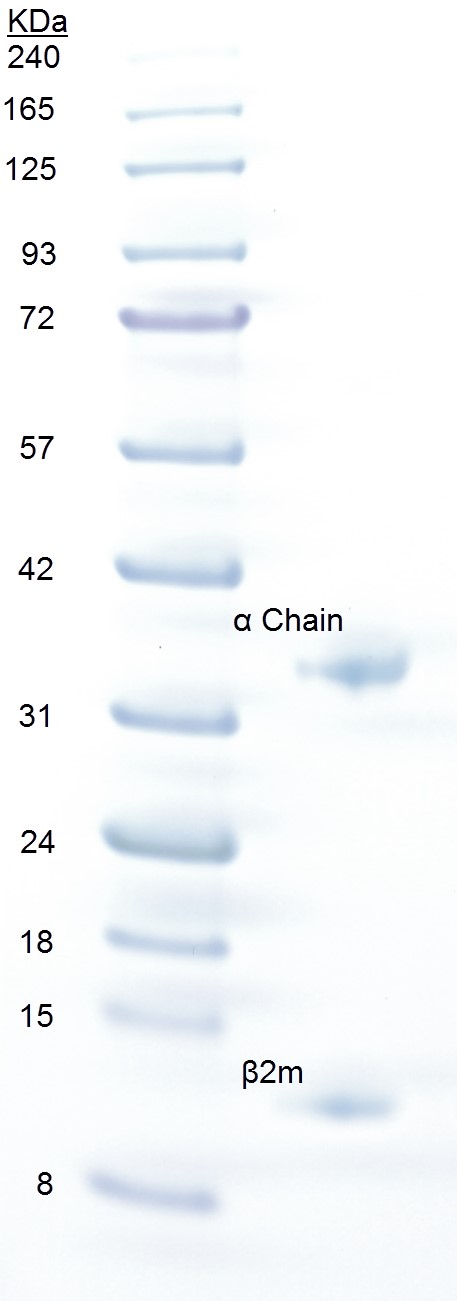
Figure 1. SDS-PAGE analysis of pMHCI. Approximately 20 µg of pMHCI (right lane) was loaded onto a 4-12% gradient Bolt® Bis-Tris gel with 3 µl BLUeye prestained protein ladder (left lane) and run at 200 V for 23 min in NuPAGE MES running buffer. The gel was stained for 5 min in Quick Coomassie Stain and destained with ddH2O. The pMHCI α chain runs as a separate band at ~32 kDa and β2m at ~12 kDa.
- Prepare a 500 ml solution of PBS using 1 tablet per 100 ml of ultra-pure water. With the bottle top filtration device and vacuum pump, filter this solution through a cellulose nitrate 0.45 µm filter paper, with a 1.2 µm glass microfiber filter as a pre-filter, into a 500 ml Duran bottle. Prepare another 500 ml Duran bottle of ultra-pure water.
- Determination of parameters
- Record UV spectra of the supernatant (step A7) from 360 to 230 nm in a 1-cm quartz cuvette with the buffer baseline subtracted. Within the 360 to 320 nm range, the absorbance should be essentially zero; any slope is due to light scattering indicating the presence of large aggregates.
- Calculate the 280 nm absorption coefficient based on the amino acid composition (Pace et al., 1995) using the ProtParam website at http://web.expasy.org/protparam/.
Due to the high amount of the aromatic residues Tyr (5.3%) and Trp (3.2%) within the HLA-A2 and β2-microglobulin sequences combined (see Supplements 1 and 2), a good estimate for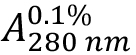 (absorption coefficient) can be expected. As HLA-A2 and β2-microglobulin have two and one intra-chain disulphide bonds, respectively, the cystine contribution to the absorption is included (ProtParam option: ‘assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines’).
(absorption coefficient) can be expected. As HLA-A2 and β2-microglobulin have two and one intra-chain disulphide bonds, respectively, the cystine contribution to the absorption is included (ProtParam option: ‘assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines’). - Calculate protein concentration from the measured optical density at 280 nm
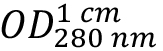 as:
as: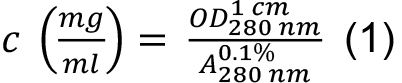
- Use ProtParam to calculate the molecular mass based on the average isotopic masses of amino acids. All three sequences of the HLA-A2/β2m/peptide complex are entered into the program input field together. To account for the two missing peptide bonds due to the three instead of single chain complex as seen by the program, two times the molecular mass of water (2 x 18.02) is added to the resulting mass Mr.
- Calculate the mean residue weight (MRW) required for the normalization of the CD data from this mass by dividing the number of peptide bonds:
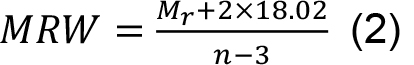
where, n is the number of amino acids within the trimer.
- Record UV spectra of the supernatant (step A7) from 360 to 230 nm in a 1-cm quartz cuvette with the buffer baseline subtracted. Within the 360 to 320 nm range, the absorbance should be essentially zero; any slope is due to light scattering indicating the presence of large aggregates.
- Data acquisition
- Based on the concentration of the stock solution determined as described above, dilute an aliquot with buffer to result in ca. 600 μl of sample with c ~0.15 mg/ml (~3 μM), and record a further absorption spectrum to give the final protein concentration (Note 2).
- Following the usual start-up procedure of the CD instrument (30 min flushing with N2 followed by a further 30 min period for stabilizing the xenon arc lamp), record a spectrum of the buffer (step A1) in a clean 0.1-cm stoppered quartz cell from 260 to ~195 nm with the cell holder equilibrated to 4 °C. This spectrum is termed the baseline. We usually record spectra using a 1 nm bandwidth in 0.2 nm intervals with 3 or 4 sec measuring time per data point resulting in ca. 20 to 25 min per spectrum (Note 3).
- Record a further buffer baseline in the Kinetic Mode at a constant wavelength of 218 nm for 1 min in 2 sec intervals.
- Clean the cell with water by rinsing, followed by rinsing with absolute ethanol and dried under a stream of nitrogen.
- Fill the same cell completely with the protein solution (~550 μl), closed tightly with a Teflon stopper avoiding trapping of an air bubble, and place into the CD cell holder in the same orientation as used for recording the baseline.
- After ~2 min to allow for temperature equilibration, record the protein spectrum using the same instrument settings as used for the baseline. Data are reliable if the photomultiplier dynode voltage is < 500 V (Note 4).
- For temperature denaturation, set the wavelength to 218 nm (minimum in CD spectrum). Record changes in ellipticities in 0.5 °C intervals from 4 to ~80 °C using the following parameters: data collection 12 sec/point; temperature equilibration 12 sec; temperature dead band 0.3 °C; instrument heating rate 4 °C/min. During the intervals between data collection, the sample is shielded from the light beam by a closed slit. These settings result in an average heating rate of ~36 °C/h (Note 5).
- At elevated temperatures the HLA-A2/β2m/peptide complexes form large, visible aggregates (precipitation) that result in sharp changes of the melting profile and an increase of the dynode voltage indicating increased scattering. At this point, the measurement can be stopped.
- Clean protein precipitate containing cuvettes thoroughly rinsing with water followed by filling with 70% HNO3 in a fume hood, incubation for 2 h to overnight, rinsing with water, ethanol, and drying with a stream of N2.
- Based on the concentration of the stock solution determined as described above, dilute an aliquot with buffer to result in ca. 600 μl of sample with c ~0.15 mg/ml (~3 μM), and record a further absorption spectrum to give the final protein concentration (Note 2).
Data analysis
- Import CD data files into the OriginLab software (Note 6).
- For spectra analysis, subtract the buffer baseline. Normalise Θ values recorded in mdeg to molar ellipticities [Θ]MRW in the classical units (deg cm2 dmol-1) according:
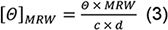
with the concentration c in mg/ml and cell path length d in mm (Note 7). - Subtract the mean of Θ recorded at 218 nm in the Kinetic Mode (step C3) from the thermal melt ellipticities, and normalize to [Θ]MRW218nm according to Eq. (3).
- Analysis of the thermal stability assumes a 2-state mechanism in which three unfolded polypeptide chains U combine to a native complex N:
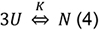
where, the equilibrium constant K is: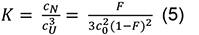
with a total chain concentration c0 = cU +3CN and a degree of conversion to the native state F = 3 CN/c0 (see e.g., Engel et al., 1977; Marky and Breslauer, 1987). The standard Gibbs free energy can be written as:
ΔG0 = -RT ln K = ΔH0 - TΔS0 (6)
in which R is the gas constant (8.3145 J K-1 mol-1), ΔH0 the standard enthalpy, and ΔS0 the standard entropy. From Eqs. (5) and (6) it follows for the midpoint of transition, where F = 0.5 and T equals the melting temperature Tm, at which half of the proteins are in the folded and unfolded state, respectively, that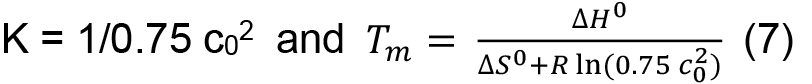
This means that in contrast to a single chain polypeptide the melting temperature is concentration dependent. Tm and ΔH0 can be obtained by fitting the entire transition curve to the van’t Hoff equation: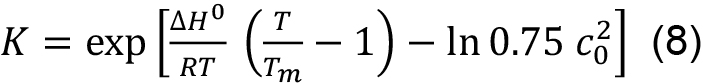
obtained by solving Eq. (7) for ΔS0 and substituting for ΔS0 in Eq. (6).
The molar ellipticities for the native and unfolded state [Θ]n and [Θ]u show an additional temperature dependence which in a first approximation can be assumed as linear:
[Θ]n = [Θ]n0 + bn T and [Θ]u = [Θ]u0 + bu T (9)
where, [Θ]n0 and [Θ]u0 correspond to the [Θ] intercept at T = 0, and bn and bu describe the slopes of the native and unfolded states, respectively. The entire transition curve is thus described by:
[Θ] = F ([Θ]n0 + bn T - [Θ]u0 - bu T) + [Θ]u0 + bu T (10)
which is used for fitting with the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm implemented in OriginLab. The essential parts of the fitting script are included as Supplement 4. - As the HLA-A2/β2m/peptide complexes tend to precipitate within the transition region (step C8), we assume a common molar ellipticity [Θ]u0 = -4,500 deg cm2 dmol-1 and slope bu = 0. For many temperature denatured proteins and model peptides [Θ]u0 values in the -4,000 to -5,000 deg cm2 dmol-1 range are observed (Venyaminov et al., 1993) (Notes 8 and 9).
- Representative data
The general procedure to analyse the stability of a trimeric pMHC complex is illustrated using HLA-A2/β2m/ILAKFLHWL as an example (Figure 2).This complex has been analysed in detail (Cole et al., 2017) and the structure has been solved in complex with a TCR (Protein Data Bank entry 5MEN).
Figure 2. Thermal stability of HLA A2/β2m/ILKA. A. Protein concentration is determined by UV absorbance spectroscopy. Wavelength scans from 360 to 230 nm are recorded in a 1-cm quartz cuvette using the same sample and buffer as used in subsequent CD measurements. Concentration is calculated assuming an absorbance coefficient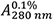 = 2.257 as calculated based on the amino acid composition. B. A far-UV CD spectrum was recorded in a 0.1-cm quartz cuvette at 4 °C and buffer baselines measured in the same cell using the same instrument parameters were subtracted. The signals were normalized to mean-residue-weight (MRW) ellipticities [Θ]MRW acc. Eq. (3). C. Thermal stability was determined by following the ellipticity Θ at 218 nm upon increasing the temperature with measuring 12 sec per data point in ΔT = 0.5 °C intervals, an equilibration time of 12 sec between data points, a temperature dead band of ± 0.3 °C, and using slit closure between measurements resulting in a mean heating rate of 36 °C/h (red, left axis). The sample forms large, visible aggregates indicating precipitation in the 58 to 65 °C range (open circles). Data points below this temperature (filled circles) were fitted acc. Eq. (10) resulting in the dashed curve. Aggregate formation is accompanied by increasing light scattering resulting in a steep increase of the dynode voltage (blue, right axis) followed by a decrease when large particles sink to the bottom of the cuvette.
= 2.257 as calculated based on the amino acid composition. B. A far-UV CD spectrum was recorded in a 0.1-cm quartz cuvette at 4 °C and buffer baselines measured in the same cell using the same instrument parameters were subtracted. The signals were normalized to mean-residue-weight (MRW) ellipticities [Θ]MRW acc. Eq. (3). C. Thermal stability was determined by following the ellipticity Θ at 218 nm upon increasing the temperature with measuring 12 sec per data point in ΔT = 0.5 °C intervals, an equilibration time of 12 sec between data points, a temperature dead band of ± 0.3 °C, and using slit closure between measurements resulting in a mean heating rate of 36 °C/h (red, left axis). The sample forms large, visible aggregates indicating precipitation in the 58 to 65 °C range (open circles). Data points below this temperature (filled circles) were fitted acc. Eq. (10) resulting in the dashed curve. Aggregate formation is accompanied by increasing light scattering resulting in a steep increase of the dynode voltage (blue, right axis) followed by a decrease when large particles sink to the bottom of the cuvette. - Absorption coefficient and mean-residue-weight are calculated by putting all three sequences (Supplements 1 to 3) into the input frame of ProtParam (step B2) resulting in:
Number of amino acids: 386
Molecular weight: 44820.03
.....
Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm measured in water.
Ext. coefficient 101675
Abs 0.1% (=1 g/L) 2.269, assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines - The measured absorption of the protein solution (Figure 2A) shows
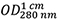 = 0.283 resulting with Eq. (1) in a concentration of 0.283/2.269 = 0.125 mg/ml.
= 0.283 resulting with Eq. (1) in a concentration of 0.283/2.269 = 0.125 mg/ml. - MRW is calculated according to Eq. (2) as MRW = (44,820.03 + 2 x 18.02)/(386 - 3) = 117.12.
- A CD buffer baseline and spectra of both solutions are recorded according to steps C2 to C6 using a 0.1-cm path length cuvette. Baselines were subtracted, and the spectrum is normalised according to Eq. (3) (Figure 2B). At 195 nm, the dynode voltage was ~500 V. This reflects the high absorbance of the chloride ion included in PBS. The spectrum shows a minimum of [Θ]MRW = -8,950 deg cm2 dmol-1 at 218 nm.
- The melting curve is recorded as described in step C7 from 4 to 65 °C, the mean value of the baseline (step C3) is subtracted, and molar residue ellipticities calculated according to Eq. (3) (Figure 2C). Using the OriginLab script given as Supplement 4 fit the data according to Eq. (10). Values in the 59 to 65 °C range that show a pronounced deviation from a homogenous quasi-sigmoidal curve indicating protein aggregation (open dots in Figure 2C) were omitted from the fits. Fitting results in Tm = 54.5 ± 0.1 °C and ΔH0 = -500 ± 20 kJ/mol with a coefficient of determination r2 = 0.988.
Notes
- Peak fractionation of the pMHC will occur at an elution volume of ~12 ml; it is important to keep only the purest fractions and discard any that contain protein from more than one peak.
- To determine thermodynamic parameters, for HLA-A2/β2m/peptide complexes we aim for a concentration of ~0.15 mg/ml as for most peptides studied so far this can be relatively easily achieved and provides for a good signal-to-noise ratio to follow CD transition curves at 218 nm. Due to the concentration dependence of Tm for multi-chain proteins [Eq. (7)], it is important to settle for a narrow range to allow for comparison of data.
- A cuvette can be regarded as optically clean if the baseline using PBS or water runs about parallel to a spectrum recorded without a cell in the light beam (‘air baseline’); minima observed in the 200 to 225 nm range usually indicate that protein from previous measurements is absorbed to the quartz surface.
- On instruments of other manufacturers, the dynode voltage is called HT (high tension), and the reliable voltage range can differ depending on the type of photomultiplier and electronics.
- The heating parameters have been tested to result in the set equilibrium temperatures by measuring with a Pt100 Resistance Temperature Detector inside a 0.1-cm cuvette.
- The AVIV instrument software stores data in ASCII format. Some instruments from other manufacturers use propriety formats that require exporting into ASCII for analysis via other programs.
- [Θ]MRW can be converted into molar absorption units Δε = εL - εR = [Θ]MRW/3,298, where Δε is the absorption difference for left- and right-handed circularly polarized light.
- From the various MHC complexes studied in our lab, HLA-A*0101/β2m/peptide VTEHDTLLY exhibit high stability both with respect to Tm (68.9 °C) and enthalpy (-719 kJ mol-1); precipitation occurred only at T > 72 °C, [Θ]U0 > -5,200 deg cm2 dmol-1 (Jones et al., 2016). Using [Θ]U0 = -4,500 deg cm2 dmol-1 resulted in a r2 > 0.996.
- For strict thermodynamic analysis reversibility of the transition [Eq. (4)] is a prime requirement. It has been suggested, however, that even if reversibility is limited analysis is still of value as temperature induced cooperative unfolding is usually a much faster process than the aggregation of unfolded protein (Privalov, 2009). To allow for comparison of data, we use the same heating parameters for all samples (see step C7).
Acknowledgments
DKC is a Wellcome Trust Research Career Development Fellow (WT095767). AKS is a Wellcome Trust Senior Investigator. This and original work using the described procedures was supported by the UK Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) (Grant BB/H001085/1). Purchase of the CD instrument was partially funded by BBSRC grant 75/REI18433.
References
- Bronke, C., Almeida, C. A., McKinnon, E., Roberts, S. G., Keane, N. M., Chopra, A., Carlson, J. M., Heckerman, D., Mallal, S. and John, M. (2013). HIV escape mutations occur preferentially at HLA-binding sites of CD8 T-cell epitopes. AIDS 27(6): 899-905.
- Bulek, A. M., Cole, D. K., Skowera, A., Dolton, G., Gras, S., Madura, F., Fuller, A., Miles, J. J., Gostick, E., Price, D. A., Drijfhout, J. W., Knight, R. R., Huang, G. C., Lissin, N., Molloy, P. E., Wooldridge, L., Jakobsen, B. K., Rossjohn, J., Peakman, M., Rizkallah, P. J. and Sewell, A. K. (2012). Structural basis for the killing of human beta cells by CD8+ T cells in type 1 diabetes. Nat Immunol 13(3): 283-289.
- Cole, D. K., Bulek, A. M., Dolton, G., Schauenberg, A. J., Szomolay, B., Rittase, W., Trimby, A., Jothikumar, P., Fuller, A., Skowera, A., Rossjohn, J., Zhu, C., Miles, J. J., Peakman, M., Wooldridge, L., Rizkallah, P. J. and Sewell, A. K. (2016). Hotspot autoimmune T cell receptor binding underlies pathogen and insulin peptide cross-reactivity. J Clin Invest 126(6): 2191-2204.
- Cole, D. K., Edwards, E. S., Wynn, K. K., Clement, M., Miles, J. J., Ladell, K., Ekeruche, J., Gostick, E., Adams, K. J., Skowera, A., Peakman, M., Wooldridge, L., Price, D. A. and Sewell, A. K. (2010). Modification of MHC anchor residues generates heteroclitic peptides that alter TCR binding and T cell recognition. J Immunol 185(4): 2600-2610.
- Cole, D. K., Pumphrey, N. J., Boulter, J. M., Sami, M., Bell, J. I., Gostick, E., Price, D. A., Gao, G. F., Sewell, A. K. and Jakobsen, B. K. (2007). Human TCR-binding affinity is governed by MHC class restriction. J Immunol 178(9): 5727-5734.
- Cole, D. K., van den Berg, H. A., Lloyd, A., Crowther, M. D., Beck, K., Ekeruche-Makinde, J., Miles, J. J., Bulek, A. M., Dolton, G., Schauenburg, A. J., Wall, A., Fuller, A., Clement, M., Laugel, B., Rizkallah, P. J., Wooldridge, L. and Sewell, A. K. (2017). Structural mechanism underpinning cross-reactivity of a CD8+ T-cell clone that recognizes a peptide derived from human telomerase reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem 292(3): 802-813.
- Engel, J., Chen, H. T., Prockop, D. J. and Klump, H. (1977). The triple helix in equilibrium with coil conversion of collagen-like polytripeptides in aqueous and nonaqueous solvents. Comparison of the thermodynamic parameters and the binding of water to (L-Pro-L-Pro-Gly)n and (L-Pro-L-Hyp-Gly)n. Biopolymers 16(3): 601-622.
- Jávorfi, T., Hussain, R., Myatt, D. and Siligardi, G. (2010). Measuring circular dichroism in a capillary cell using the b23 synchrotron radiation CD beamline at diamond light source. Chirality 22 Suppl 1: E149-153.
- Jones, K., Wockner, L., Brennan, R. M., Keane, C., Chattopadhyay, P. K., Roederer, M., Price, D. A., Cole, D. K., Hassan, B., Beck, K., Gottlieb, D., Ritchie, D. S., Seymour, J. F., Vari, F., Crooks, P., Burrows, S. R. and Gandhi, M. K. (2016). The impact of HLA class I and EBV latency-II antigen-specific CD8+ T cells on the pathogenesis of EBV+ Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Exp Immunol 183(2): 206-220.
- Kløverpris, H. N., Cole, D. K., Fuller, A., Carlson, J., Beck, K., Schauenburg, A. J., Rizkallah, P. J., Buus, S., Sewell, A. K. and Goulder, P. (2015). A molecular switch in immunodominant HIV-1-specific CD8 T-cell epitopes shapes differential HLA-restricted escape. Retrovirology 12: 20.
- Knight, R. R., Dolton, G., Kronenberg-Versteeg, D., Eichmann, M., Zhao, M., Huang, G. C., Beck, K., Cole, D. K., Sewell, A. K., Skowera, A. and Peakman, M. (2015). A distinct immunogenic region of glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 is naturally processed and presented by human islet cells to cytotoxic CD8 T cells. Clin Exp Immunol 179(1): 100-107.
- Latron, F., Pazmany, L., Morrison, J., Moots, R., Saper, M. A., McMichael, A. and Strominger, J. L. (1992). A critical role for conserved residues in the cleft of HLA-A2 in presentation of a nonapeptide to T cells. Science 257(5072): 964-967.
- MacLachlan, B.J., Greenshields-Watson, A., Mason, G.H., Schauenburg, A.J., Bianchi, V., Rizkallah, P.J., Sewell, A.K., Fuller A. and Cole, D.K. (2017). Using X-ray crystallography, biophysics, and functional assays to determine the mechanisms governing T-cell receptor recognition of cancer antigens. J Vis Exp. 6(120).
- Marky, L. A. and Breslauer, K. J. (1987). Calculating thermodynamic data for transitions of any molecularity from equilibrium melting curves. Biopolymers 26(9): 1601-1620.
- Motozono, C., Pearson, J. A., De Leenheer, E., Rizkallah, P. J., Beck, K., Trimby, A., Sewell, A. K., Wong, F. S. and Cole, D. K. (2015). Distortion of the major histocompatibility complexclass I binding groove to accommodate an insulin-derived 10-Mer peptide. J Biol Chem 290(31): 18924-18933.
- Pace, C. N., Vajdos, F., Fee, L., Grimsley, G., and Gray, T. (1995). How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci 4(11): 2411-2423.
- Parker, K. C., Bednarek, M. A., Hull, L. K., Utz, U., Cunningham, B., Zweerink, H. J., Biddison, W. E. and Coligan, J. E. (1992). Sequence motifs important for peptide binding to the human MHC class I molecule, HLA-A2. J Immunol 149(11): 3580-3587.
- Privalov, P. L. (2009). Microcalorimetry of proteins and their complexes. Methods Mol Biol 490: 1-39.
- Venyaminov S. Yu., Baikalov I. A., Shen, Z. M., Wu, C. S., and Yang, J. T. (1993). Circular dichroic analysis of denatured proteins: inclusion of denatured proteins in the reference set. Anal Biochem. 214(1):17-24.
- Yin, Y., Li, Y., Kerzic, M. C., Martin, R. and Mariuzza, R. A. (2011). Structure of a TCR with high affinity for self-antigen reveals basis for escape from negative selection. EMBO J 30(6): 1137-1148.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Fuller, A., Wall, A., Crowther, M. D., Lloyd, A., Zhurov, A., Sewell, A. K., Cole, D. K. and Beck, K. (2017). Thermal Stability of Heterotrimeric pMHC Proteins as Determined by Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy. Bio-protocol 7(13): e2366. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2366.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell staining > Immunodetection
Cell Biology > Cell staining > Protein
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link