- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Isolation and Culturing of Rat Primary Embryonic Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons (BFCNs)
Published: Vol 7, Iss 14, Jul 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2413 Views: 5993
Reviewed by: Jia LiAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Human Schwann Cells in vitro I. Nerve Tissue Processing, Pre-degeneration, Isolation, and Culturing of Primary Cells
Gabriela I. Aparicio and Paula V. Monje
Nov 20, 2023 512 Views
Three-dimensional Co-culture Model for Live Imaging of Pancreatic Islets, Immune Cells, and Neurons in Agarose Gel
Elke M. Muntjewerff [...] Gustaf Christoffersson
Oct 20, 2023 707 Views
Generation of Mouse Primitive Endoderm Stem Cells
Yasuhide Ohinata [...] Haruhiko Koseki
Nov 20, 2023 238 Views
Abstract
The basal forebrain is located close to the medial and ventral surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres that develop from the sub-pallium. It regulates multiple processes including attention, learning, memory and sleep. Dysfunction and degeneration of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons (BFCNs) are believed to be involved in many disorders of the brain such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), schizophrenia, sleep disorders and drug abuse (Mobley et al., 1986). Primary cultures of BFCNs will provide an important tool for studying the mechanism of these diseases. This protocol provides a detailed description of experimental procedures in establishing in vitro primary culture of rat embryonic BFCNs.
Keywords: Basal forebrain cholinergic neuronBackground
The basal forebrain cholinergic system innervates the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. The normal function of the BFCNs is essential for normal sleeping, learning and memory. And the atrophy of BFCNs is considered as the early event of Alzheimer’s disease. Thus, the primary BFCNs culture will be the ideal cell model for AD research. In previous studies, primary BFCNs cultures were rarely used. Here, we present a reliable method to isolate and culture BFCNs from the embryonic rat septum which is simple, less time consuming than the previous method (Schnitzler et al., 2008). Our method will greatly facilitate studies of many critical aspects of BFCN function and cell biology.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips
- Coverglasses (Thermo Fisher Scientific or VWR)
- Falcon tubes (50 ml)
- Falcon tubes (15 ml)
- Sterile pipettes 5, 10, 25 ml
- 12-well culture plate
- 10, 15 cm cell culture dishes
- Razor blades
- Fire-polished glass Pasteur pipettes
Note: Materials #3-9 can be from various suppliers.
- Microfluidic chamber (XONA MICROFLUIDICS, catalog number: SND450 )
- Stericup® filter units (150, 250 ml) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: SCVPU02RE , 0.10 µm, polyethersulfone)
- Pregnant female Sprague Dawley rats (Embryos dissected at E17.5) (Harlan Sprague Dawley)
- Poly-L-lysine 0.1% (w/v) in dH2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8920 )
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (without CaCl2, MgCl2) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 1419094 )
- 70% ethanol
- 10x, 2.5% trypsin, no phenol red (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15090046 )
- 10x DNase I (10 mg/ml) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 10104159001 )
- Anti-TrkA antibody
- 10x Hanks’ balanced salt solution (HBSS) w/o PR, sod.bicarb, CaMg (Mediatech, catalog number: 20-023-CV )
- Penicillin-streptomycin (100x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15140122 )
- Neurobasal-A medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10888022 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Qmega Scientific, catalog number: FB-02 or various suppliers) (heat in activation before use)
- 50x B27 supplement (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 17504044 )
- 100x GlutaMAX (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 35050061 )
- Mouse purified NGF as previously published (Mobley et al., 1986)
- Dissection buffer (see Recipes)
- Plating media (see Recipes)
- Maintenance media (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Sterile cell culture hood (Esco Micro, model: Class II Type A2 )
- Scissors
- #5 biologie forces and small spring scissors (Fine Science Tools)
- Pipette
- Water bath (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: PrecisionTM Model 281 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Cell culture incubator (Panasonic, model: MCO-19AIC UV-PA )
- Dissecting microscope (Leica, model: Leica S8 AP0 )
- Cell culture centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: CL2 )
- Autoclave (STERIS, model: AMSCO® Evolution® Steam Sterilizer )
Procedure
- Preparation
- Coat plates/coverglasses using poly-L-lysine (PLL) for 12 h at 4 °C or for 2-4 h at 37 °C. The coverglasses are immersed in PLL in a 10 cm cell culture plate. For coating 12-well culture plates, 0.5 ml of PLL is added to each well to cover the whole surface.
- Wash 3-4 x with 1 ml cold PBS followed by a quick rinse with 1 ml sterile water, and air dry the plate or coverglasses in the sterile cell culture hood.
- Disinfect all dissection tools in 70% ethanol.
- Coat plates/coverglasses using poly-L-lysine (PLL) for 12 h at 4 °C or for 2-4 h at 37 °C. The coverglasses are immersed in PLL in a 10 cm cell culture plate. For coating 12-well culture plates, 0.5 ml of PLL is added to each well to cover the whole surface.
- Embryo dissections (all procedures have been approved by UCSD IACUC)
One Sprague Dawley female pregnant rat (E17.5)- Anesthetize the rat in an approved CO2 chamber.
- Perform cervical dislocation.
- Disinfect the rat’s abdomen with 70% ethanol.
- Cut the skin with scissors in a T fashion, posterior to anterior direction followed by an intersecting cut right above the genital area.
- Cut the muscle tissue in a similar pattern.
- Locate the horns of the uterus and sever with scissors, remove the uterus.
- Place uterus in a 10 cm TC dish and cut along the uterus freeing each embryo in its amniotic sac and placenta.
- Remove each embryo from its amniotic sac and transfer to a 10 cm TC dish with 10-15 ml 1x HBSS to cover all embryos. Place this dish on ice.
- Anesthetize the rat in an approved CO2 chamber.
- BFCNs dissections
- Place an embryo into a 10 cm TC dish on ice. And the following dissection procedures are performed either at room temperature or on ice.
- Remove the head with a razor blade.
- Use #5 biologie forceps to cut the skin and soft bones to expose the whole brain.
- Gently extract the brain and put it on a 10 cm TC dish.
- Cut and remove the olfactory tubercles, cerebellum and brain stem.
- Carefully remove the meninges membrane (meninges will become separate from the brain and become more visible when the tissue is immersed in 1x HBSS, starting from the edge of the tissue, use forceps to carefully peel the reddish membrane off the brain, as complete as possible).
- The basal forebrain is just located close to the medial and ventral surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres.
- Gently open the cerebral hemispheres along the sagittal suture to expose the diencephalon and the basal forebrain.
- Make a transversal cut to separate the posterior side of the basal forebrain from the anterior pole of the diencephalon.
- Place the basal forebrain tissues in a 15 ml tube with 1x HBSS and place the tube in ice.
- Repeat steps C1-C9 and collect all the BFCN tissues.
- Place an embryo into a 10 cm TC dish on ice. And the following dissection procedures are performed either at room temperature or on ice.
- Mechanical/enzymatic dissociation of BFCNs
- Wash the BFCN tissues with 5 ml cold 1x HBSS, repeat for 4 times.
- Remove the buffer by pipette.
- Add 1.8 ml 1x HBSS, 0.2 ml 10x trypsin (2.5%).
- Incubate for 15 min in a 37 °C water bath.
- Add 0.2 ml 10x DNase (10 mg/ml) and gently pipette up and down 10-15 times with a fire-polished glass Pasteur pipette until the mixture becomes homogenous suspension with no visible undigested tissues.
- Pre-warm plating media at 37 °C before use.
- Add 5 ml pre-warmed plating media and spin for 5 min at 500 x g (or 1,000 rpm) at room temperature.
- Remove supernatant.
- Add plating media (volume determined by desired plating density/method).
Note: 500 µl per well for 12-well plate or 150 µl for coverglass. - After 30 min, add 1 ml plating media and put into a 37 °C CO2 incubator.
- Change to maintenance media the next day. The cultures can be maintained for 10-14 days with half the media changed to fresh media every other day.
- Wash the BFCN tissues with 5 ml cold 1x HBSS, repeat for 4 times.
Data analysis
Neurons can be cultured in microfluidic chamber (Figure 1A, left panel: a DIC image; right panel: an image of immunostaining with anti-TrkA antibody) to separate neuronal soma from long axons to study axonal transport. Neurons can also be grown in mass culture on coated coverglasses for other applications. For instance, immunostaining was used to confirm the presence of cholinergic (at DIV7), NGF-responsive neurons in the culture with specific antibodies against choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), a marker for cholinergic neurons, and TrkA, the receptor for NGF (Figure 1B). The majority of neurons (> 90%) were positive for both markers (Xu et al., 2016).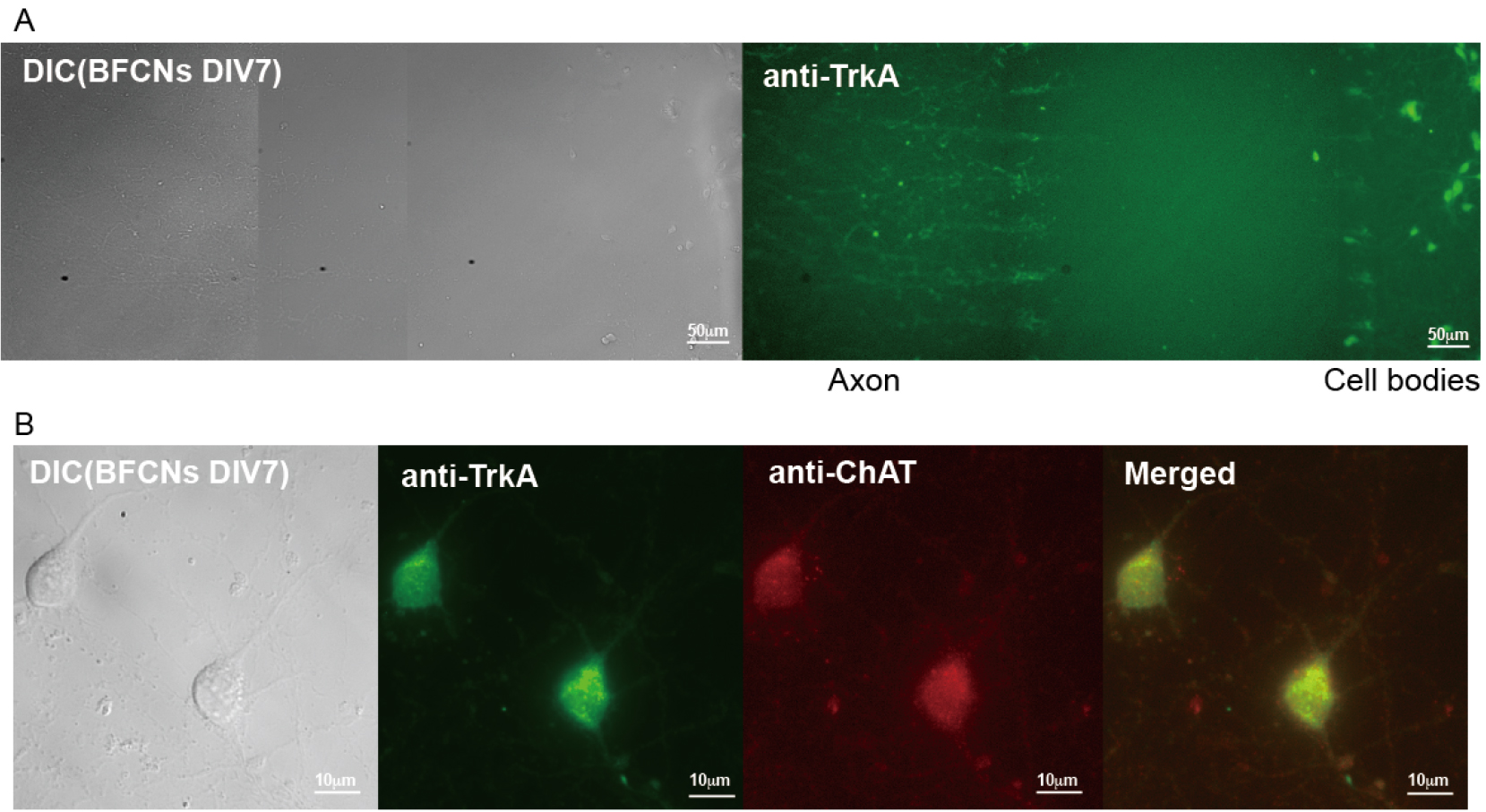
Figure 1. Cultures of rat E18 basal forebrain cholinergic neurons (BFCNs). A. Representative images of primary BFCNs (DIV7) (left: DIC; right: anti-TrkA immunostaining) cultured in microfluidic chamber. Scale bars = 50 μm. B. Representative images of primary BFCNs (DIV7) were costained for the cholinergic neuronal marker ChAT (red) and the NGF receptor TrkA (green). Scale bars = 10 μm.
Note: For representative photos and results please refer to (Xu et al., 2016).
Recipes
- Dissection buffer (filter sterilized)
10 ml 10x Hanks’ balanced salt solution (HBSS)
89 ml ddH2O
1 ml Pen/Strep - Plating media (filter sterilized)
43.5 ml Neurobasal media
5 ml FBS
1 ml 50x B27
0.5 ml 100x GlutaMAX
3.Maintenance media
Plating media plus 50 ng/ml NGF (final concentration)
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from methods described by Schnitzler et al. (2008). The study is supported by the following grants: NIH (PN2EY016525), NIH UCSD ADRC P50 Pilot grant, Down Syndrome Research and Treatment Foundation, Larry L. Hillblom Foundation, Tau Consortium, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (2014CB965002, 2012BAI10B03), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81171200), Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (13JC1401502, 13140904000), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (12ZZ115).
References
- Mobley, W. C., Rutkowski, J. L., Tennekoon, G. I., Gemski, J., Buchanan, K. and Johnston, M. V. (1986). Nerve growth factor increases choline acetyltransferase activity in developing basal forebrain neurons. Brain Res 387(1): 53-62.
- Pacifici, M. and Peruzzi, F. (2012). Isolation and culture of rat embryonic neural cells: a quick protocol. J Vis Exp (63): e3965.
- Schnitzler, A. C., Lopez-Coviella, I. and Blusztajn, J. K. (2008). Purification and culture of nerve growth factor receptor (p75)-expressing basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Nat Protoc 3(1): 34-40.
- Xu, W., Weissmiller, A. M., White, J. A., 2nd, Fang, F., Wang, X., Wu, Y., Pearn, M. L., Zhao, X., Sawa, M., Chen, S., Gunawardena, S., Ding, J., Mobley, W. C. and Wu, C. (2016). Amyloid precursor protein-mediated endocytic pathway disruption induces axonal dysfunction and neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest 126(5): 1815-1833.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Xu, W. and Wu, C. (2017). Isolation and Culturing of Rat Primary Embryonic Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons (BFCNs). Bio-protocol 7(14): e2413. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2413.
Category
Neuroscience > Cellular mechanisms > Cell isolation and culture
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link