- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Eye Drops for Delivery of Bioactive Compounds and BrdU to Stimulate Proliferation and Label Mitotically Active Cells in the Adult Rodent Retina
(*contributed equally to this work) Published: Vol 8, Iss 21, Nov 5, 2018 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3076 Views: 4658
Reviewed by: Vivien Jane Coulson-ThomasRumen IvanovAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Isolation, Culture, and Identification of Primary Müller Cells from Human Retina
Yingying Chen [...] Ling Zhu
Oct 5, 2021 2157 Views
Maximizing the Rod Outer Segment Yield in Retinas Extracted from Cattle Eyes
Isabella Panfoli [...] Alberto Diaspro
Jul 20, 2022 1044 Views
A Modified Acyl-RAC Method of Isolating Retinal Palmitoyl Proteome for Subsequent Detection through LC-MS/MS
Sree I. Motipally [...] Saravanan Kolandaivelu
Apr 20, 2023 647 Views
Abstract
Eye drop treatments are typically used to apply drugs to the anterior structures of the eye. Recently, however, studies have demonstrated that eye drops can reach the retina in the back of the eye if pharmacological agents are carried in appropriate vehicles. Here, we introduce an eye drop procedure to deliver a drug (PNU-282987), in combination with BrdU, to stimulate cell cycle re-entry and label dividing cells in the retinas of adult rodents. This procedure avoids potential systemic complications of repeated intraperitoneal injections, as well as the retinal damage that is induced by repeated intravitreal injections. Although the delivery of PNU-282987 and BrdU is the focus of this article, many different proliferating compounds could be delivered to the retina using this procedure.
Keywords: BrdUBackground
Although eye drop applications are not considered innovative, they are typically used to generate effects in the anterior portion of the eye (Patel et al., 2013; Sung et al., 2015). For instance, eye drop medications used in glaucoma patients decrease the production of aqueous humor or affect drainage of fluid through the trabecular meshwork in the anterior chamber of the eye (Dikopf et al., 2017). However, others have begun to use agents that are dissolved in vehicles to exert their effects in the back of the eye at the retina. For instance, the neuropeptide pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide [PACAP] provides a well-established neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects in the eye against different retinopathies. Although the route of delivery is usually intravitreal, a recent study that used PACAP dissolved in benzalkonium-chloride was able to cross the ocular barriers and exert protection in ischemic conditions (Werling et al., 2017). Other studies showed that the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor specific agonist, PNU-282987 (Bodnar et al., 2005; Hajos et al., 2005; Iwamoto et al., 2014), was able to cross ocular barriers and induce neurogenesis of adult mammalian neurons when delivered as eye drops, made by diluting a stock solution of PNU-282987 in lipophilic vehicle, DMSO, in PBS. (Webster et al., 2017). Previous dose and time-dependent studies showed that PNU-282987 was detectable in the retina by HPLC MS/MS after eye drop delivery. PNU-282987 levels were detected in the retina after topical application of the nAChR agonist to the bulbar conjunctiva (Mata et al., 2015).
BrdU is a synthetic nucleoside that is an analog of thymidine and is commonly used in the detection of proliferating cells in living tissues. To label mitotically active cells with BrdU, well-established methods for delivery in rodents is via intraperitoneal or intraocular injection (Karl et al., 2008; Lee et al., 2015; Xie et al., 2016). However, more robust labeling of mitotically active cells in the retina occurs if BrdU is added into the PNU-282987 eye drop solution (Webster et al., 2017) (Figure 1). Eye drop applications of agents that reach the retina are much less invasive than either intraperitoneal or intravitreal injections and have the added advantage that they can be introduced several times each day or week without the disadvantage of multiple injections. Here, the procedure for labeling mitotically active cells in the adult rodent retina with BrdU eye drops is provided after stimulation with the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor specific agonist, PNU-282987. However, this method also has broader implications and can be used to deliver other proliferating agents in the retina. 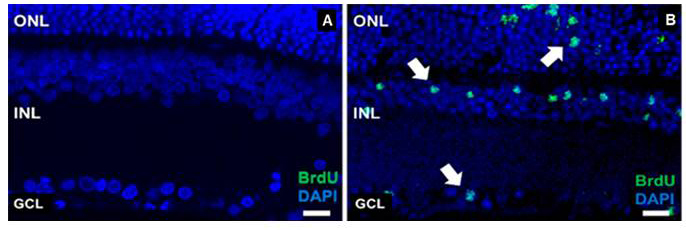
Figure 1. Evidence of successful BrdU labeling. A. A confocal retinal section obtained from an adult SVJ 129 mouse treated only with PBS containing BrdU for 3 days. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). No evidence of BrdU positive cells when the retina is processed with antibodies against BrdU. B. A confocal retinal section obtained from an eye treated with PNU-282987/BrdU eye drops for 3 days. BrdU positive cells are observed in all nuclear layers of the retina (green). ONL: outer nuclear layer, INL: inner nuclear layer, GCL: ganglion cell layer. Arrows point to BrdU positive retinal cells. Scale bars represent 50 µm.
Materials and Reagents
- 3 ml disposable transfer pipettes (VWR, catalog number: 414004-037)
- 0.2 µm sterile syringe filter (VWR, catalog number: 28145-477)
- Latex exam gloves (VWR, catalog number: 414004-429)
- Lab coat (VWR, catalog number: 37000-922)
- 3 month female adult SVJ 129 mouse
- 3 month adult female Sprague Dawley rat
- PNU-282987 (N-[(3R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-4-chlorobenzamide hydrochloride) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6499) (desiccate, store at 4 °C)
- BrdU (5-Bromo-2’-deoxyuridine) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 19-160) (store for up to 2 years at -20 °C)
- PBS (Phosphate buffered saline 10x concentrate) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5493) (store at room temperature)
- DMSO (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D8418) (store at room temperature)
- Cheerios (Local grocery store, store at room temperature)
- PNU-282987/BrdU solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 30 ml clear glass bottles (VWR, catalog number: 10862-356)
- 4 °C refrigerator
- Fume hood
Procedure
Animals are given one eye drop once a day from a backfilled 3 ml plastic disposable transfer pipette for various amounts of time depending on the experimental design of the study. One drop of solution from the transfer pipette contains 30 µl of diluted PNU-282987/BrdU. Eye drops are delivered directly to the center of the bulbar conjunctiva of the eye; a clear membrane that covers the anterior face of the sclera and the transparent surface epithelium of the cornea. A new disposable 3 ml transfer pipette is used each time eye drops are applied. Both sexes of adult rats and mice produce BrdU positive cells after 3 days of eye drop treatments. In vehicle control studies, eye drops containing PBS or eye drops containing PBS with 1% DMSO are applied as negative controls.
- Adding eye drops to adult mice
Notes:- The safe restraint and gentle handling of these rodents is a key part of the experimental procedures. All rodent handlings wear a lab coat and latex gloves in the animal facility. All handlers have Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee training before proceeding.
- Animals should be approached with confidence and the animals should be handled gently, but firmly to avoid bites or scratches to the handler or injuries to the animal.
- One handed mouse restraint is usually performed with the non-dominant hand, leaving the dominant hand free for applying eye drops.
- Lift adult mice (ranging from 3-6 months) by the base of the tail from their cage and place them on the cage lid. Tuck the base of the tail between the 3rd and 4th finger (Figure 2A).
- Then immobilize the adult mice (ranging from 3-6 months) by scruffing the skin over their neck. Using the same hand that is holding the tail, grasp the skin near the base of the head with the index finger and thumb (Figure 2B).
Note: Be sure to apply just enough pressure, or firmness, to the skin around the neck to ensure the eyes are opened and to prevent the mouse from turning or twisting out of the hand restraint. - Once the mouse is firmly scruffed, place one drop of diluted PNU-282987/BrdU solution on the bulbar conjunctiva of the right eye. The right eye should be positioned up by twisting the wrist of the restrainer’s hand. The dilution should be dropped just over the eye. Do not bring the transfer pipette in direct contact with the cornea. The drop will cover the entire eye and should sit on top of the eye as a small ball for 1-2 s (Figure 2C).
Note: If treatment is needed in the animal’s contralateral eye, the restrainer’s wrist containing the same scruffed animal should be turned so that the left eye is situated up. At this point, another single drop can be added to the left eye and allowed to sit in a small ball over the eye for 1-2 s. - Once eyes have been treated, release the animal back into its cage. It is not unusual for the animal to shake its head once it is released to remove any excess fluid that remains over its eye (see Notes).

Figure 2. Eye drop application to adult mice. A. A 3-month-old female adult SVJ 129 mouse is removed from cage and positioned for handling. B. The mouse is held for eye drop delivery. C. Eye drop applied to scruffed animal. Scale bar represents 1.25 cm.
- Adding eye drops to adult rats
- Deliver eye drops to rats (aged 3-6 months) that are not physically restrained. Remove the top of a rat cage and add an eye drop containing a dilution of PNU-282987 and BrdU to the center of the rat eye using a disposable 3 ml backfilled transfer pipette (Figure 3A). Place the eye dropper within an inch of the eye before releasing one drop of fluid containing 30 µl of diluted PNU-282987/BrdU onto the bulbar conjunctiva. The rat will blink and shake its head when an eye drop has been successfully applied. Do not allow the transfer pipette to come in direct contact with the cornea.
- When one drop has been added, a drop can also then be added to the contralateral eye depending on the experimental design of the study.
- After all drops have been administered, give each rat 2-3 Cheerios before the top of the cage is replaced (example in Figure 3B) and then return the cage containing the treated animal to the colony. All animals are housed singly.
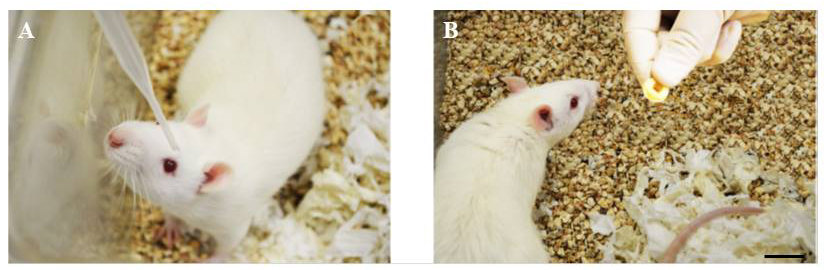
Figure 3. Eye drop application to adult rats. A. A 3-month-old adult female Sprague Dawley rat is positioned to receive one drop of PNU-282987/BrdU solution. B. The Cheerio reward is delivered after a successful eye drop delivery. Scale bar represents 2.5 cm.
Notes
The first time an eye drop is delivered to a rat eye, the animal will be unfamiliar with the procedure and may not be still long enough for an eye drop to be deposited to the center of the cornea (1-2 s is needed). To minimize this behavior, the transfer pipette containing the eye drop should be positioned and held steady above the cage until the animal settles down. The time for the animals to settle down the first time eye drops are delivered varies depending on each animal’s personality. However, the first time, it can take an average of 2 or 3 min before the animal gets use to the gloved hand holding the transfer pipette and stays still long enough to deposit an eye drop. After drops have been added to the rats two or three times however, the rats stop moving as soon as the top of the cage is removed, as they become familiar with the procedure and know they will get the Cheerio reward after its completion. Future studies may benefit from a training period for the rats to improve tolerance for getting the eye drops.
Care using BrdU:
BrdU replaces thymidine during DNA replication and can cause DNA mutations. Therefore, appropriate precautions should be taken to avoid exposure. Pregnant and lactating women should avoid exposure to BrdU and animals that have been administered BrdU eye drops. As BrdU exposure can impair the immune system; immunocompromised individuals should also use extreme caution when handling BrdU.
When eye drops are added to the animals, small amounts of solution may fall into the animal’s bedding when the animal shakes its head. This bedding should be regularly removed and autoclaved by animal facility staff that wear gloves and lab coats during the animal’s normal care. Any accidental spills of PNU-282987/BrdU should be treated with a hazardous spill kit.
Crossover:
In some instances, only one rat eye was treated with the PNU/BrdU solution, while the contralateral eye acted as an untreated control. Under these conditions, there was no evidence of crossover effects. No BrdU staining appeared in control untreated eyes (Webster et al., 2017). However, this was not the case in adult mice. When one mouse eye was treated with the PNU/BrdU solution and the contralateral eye was left untreated, crossover effects occurred. For instance, in adult mice, both eyes typically demonstrate BrdU positive cells, even if only one eye was treated with the PNU/BrdU solution. This crossover effect in mice is likely due to the relative closeness of the two eyes. As a result, contralateral eyes can be used as internal controls in adult rats, but should not be used as untreated internal controls in adult mice.
Recipes
- PNU-282987/BrdU solution
Notes:- When preparing PNU-282987 and BrdU stock solutions, latex gloves and lab coats are worn.
- Unused PNU-282987/BrdU is disposed of in a hazardous materials container.
- Preparing 10 mM PNU-282987 stock solution
A stock solution of 10 mM PNU-282987 is made using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The stock solution is kept at 4 °C for up to 3 months - Preparing BrdU stock solution
Please specify how to prepare BrdU stock solution. - When needed, the PNU-282987 stock is diluted using sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS) to various concentrations between 1 and 1,000 nM for eye drop studies
- BrdU is then added directly to the diluted PNU-282987 solution to make a final BrdU concentration of 1 mg/ml
- The final PNU-282987/BrdU solution is sterile filtered with a 0.2 µm syringe filter before use under a fume hood
- Dilutions of PNU-282987/BrdU are kept in a refrigerator at 4 °C in labeled 30 ml glass bottles for up to one week.
Acknowledgments
The funding for this procedure is provided by NIH NEI # EY022795 and EY027970 to Dr. C. Linn.
Previous studies including Webster et al. (2017) have utilized this eye drop protocol.
Competing interests
No conflicts of interest.
Ethics
Rats and mice were kept at Western Michigan University’s animal facility until needed and were cared for in accordance with the approved guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC).
References
- Bodnar, A. L., Cortes-Burgos, L. A., Cook, K. K., Dinh, D. M., Groppi, V. E., Hajos, M., Higdon, N. R., Hoffmann, W. E., Hurst, R. S., Myers, J. K., Rogers, B. N., Wall, T. M., Wolfe, M. L. and Wong, E. (2005). Discovery and structure-activity relationship of quinuclidine benzamides as agonists of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Med Chem 48(4): 905-908.
- Dikopf, M. S., Vajaranant, T. S. and Edward, D. P. (2017). Topical treatment of glaucoma: established and emerging pharmacology. Expert Opin Pharmacother 18(9): 885-898.
- Hajos, M., Hurst, R. S., Hoffmann, W. E., Krause, M., Wall, T. M., Higdon, N. R. and Groppi, V. E. (2005). The selective α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist PNU-282987 [N-[(3R)-1-Azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]-4-chlorobenzamide hydrochloride] enhances GABAergic synaptic activity in brain slices and restores auditory gating deficits in anesthetized rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312(3): 1213-1222.
- Iwamoto, K., Birkholz, P., Schipper, A., Mata, D., Linn, D. M. and Linn, C. L. (2014). A nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist prevents loss of retinal ganglion cells in a glaucoma model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55(2): 1078-1087.
- Karl, M. O., Hayes, S., Nelson, B. R., Tan, K., Buckingham, B. and Reh, T. A. (2008). Stimulation of neural regeneration in the mouse retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(49): 19508-19513.
- Lee, S. H., Kim, H. D., Park, Y. J., Ohn, Y. H. and Park, T. K. (2015). Time-dependent changes of cell proliferation after laser photocoagulation in mouse chorioretinal tissue. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56(4): 2696-2708.
- Mata, D., Linn, D. M. and Linn, C. L. (2015). Retinal ganglion cell neuroprotection induced by activation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology 99: 337-346.
- Patel, A., Cholkar, K., Agrahari, V. and Mitra, A. K. (2013). Ocular drug delivery systems: An overview. World J Pharmacol 2(2): 47-64.
- Sung, M. S., Li, Z., Cui, L., Choi, J. S., Choi, W., Park, M. J., Park, S. H. and Yoon, K. C. (2015). Effect of topical 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside in a mouse model of experimental dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 56(5): 3149-3158.
- Webster, M. K., Cooley-Themm, C. A., Barnett, J. D., Bach, H. B., Vainner, J. M., Webster, S. E. and Linn, C. L. (2017). Evidence of BrdU-positive retinal neurons after application of an Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist. Neuroscience 346: 437-446.
- Werling, D., Banks, W. A., Salameh, T. S., Kvarik, T., Kovacs, L. A., Vaczy, A., Szabo, E., Mayer, F., Varga, R., Tamas, A., Toth, G., Biro, Z., Atlasz, T. and Reglodi, D. (2017). Passage through the ocular barriers and beneficial effects in retinal ischemia of topical application of PACAP1-38 in rodents. Int J Mol Sci 18(3). pii: E675.
- Xie, D., Croaker, G. D. H., Li, J. and Song, Z. M. (2016). Reduced cell proliferation and increased apoptosis in the hippocampal formation in a rat model of Hirschsprung's disease. Brain Res 1642: 79-86.
Article Information
Publication history
Accepted: Oct 6, 2018
Published: Nov 5, 2018
Copyright
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Linn, C. L., Webster, S. E. and Webster, M. K. (2018). Eye Drops for Delivery of Bioactive Compounds and BrdU to Stimulate Proliferation and Label Mitotically Active Cells in the Adult Rodent Retina. Bio-protocol 8(21): e3076. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3076.
Category
Neuroscience > Sensory and motor systems > Retina
Cell Biology > Tissue analysis > Physiology
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link