- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Reverse Zymmogram Analysis for the Detection of Protease Inhibitor Activity
(*contributed equally to this work) Published: Vol 3, Iss 16, Aug 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.856 Views: 11354
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
High Throughput Analyses of Ascorbate-turnover Enzyme Activities in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seedlings
Lin-Bo Wu [...] Michael Frei
Oct 20, 2021 2130 Views
An in vitro Coupled Assay for PEPC with Control of Bicarbonate Concentration
Nicholas R. Moody [...] James D. Reid
Dec 20, 2021 1438 Views
An in vitro Assay to Probe the Formation of Biomolecular Condensates
Yu Zhang and Shen Lisha
Sep 5, 2023 759 Views
Abstract
This protocol describes a gel-based procedure to detect protease inhibitor activity. In this method gelatin is used as a substrate for proteolysis and is copolymerized within the polyacrylamide matrix. Protein extracts are fractioned by SDS-PAGE and then the gel is treated with the protease of interest, which degrades gelatin, except in the areas where inhibitory activity is present. Inhibition of protease activity appears as colored bands against a clear background after staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (Figure 1). The effectiveness of the assay is dependent on the capacity of the protease inhibitor to refold after SDS-PAGE fractionation. Alternatively, it can be performed using native (PAGE) gels. Although the protocol presented here has been standardized to test for subtilisin inhibitory activity, it can easily be adapted to test other proteases and protease inhibitors.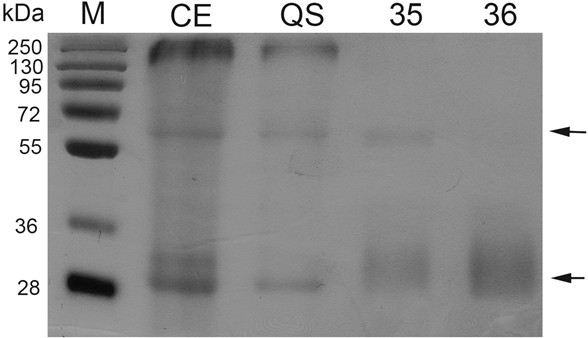
Figure 1. Protease inhibitor activity by zymogram analysis of different purified fractions and a protein crude extract. Zymogram was performed after SDS-PAGE. One microgram of protein was loaded to each lane. CE: Crude extract; QS: Fraction from anion exchange chromatography (Q-sepharose); Fractions 35-36: Obtained after a size exclusion chromatography (Superdex 200). M: Molecular markers. Arrows indicate inhibition activity.
Materials and Reagents
- Protein extract or purified protein (1-5 μg)
- Aprotinin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A-3886 )
- Subtilisin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P-5380 )
- 30% Acrylamide stock (29:1 acrylamide:bisacrylamide) (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- TEMED (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Ammonium persulfate (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- SDS (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Tris base (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Gelatin (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Bromophenol Blue (Sigma-Aldrich)
- β-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Glycine (Sigma-Aldrich)
- EDTA (JT Baker)
- Glycerol (JT Baker)
- Pre-stain Protein Standard (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Coomassie blue G250 (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Ethanol (JT Baker)
- Phosphoric acid (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Separating gel buffer (8x) (see Recipes)
- Stacking gel buffer (4x) (see Recipes)
- Gelatin-SDS-PAGE Separating gel (see Recipes)
- Stacking gel (see Recipes)
- Sample loading buffer (see Recipes)
- Laemmli Reservoir buffer (see Recipes)
- Stain solution (4 L) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Protein mini gel cassettes (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Power supply
- Orbital shaker
- Incubator
Procedure
- Preparation of the gelatin-SDS-PAGE gel
- Clean and completely dry glass plates, combs, spacers (0.75-1 mm), and assemble the gel cassette.
- Dissolve 1% gelatin in dH2O by heating, and keep warm to avoid gelling.
- Prepare the 12.5% separating gel, replacing the corresponding volume of water with the gelatin solution to a final concentration of 0.1%. Mix well and quickly transfer to the casting chamber to avoid the uneven gelling of the gelatin. Add a small layer of water or isopropanol prior to polymerization to level the gel.
- Once the gel has polymerized remove the water or isopropanol layer and dry off as much as possible by using a filter paper. Prepare and pour the stacking solution into the casting chamber and insert the comb.
- Sample Preparation.
- Add the same volume of 2x protein sample loading buffer to each protein extract to be tested, and mix. Do not heat at any time.
- Use a protein-based protease inhibitor as a positive control for the reaction, such as: aprotinin for subtilisin, or trypsin inhibitor for trypsin and load it at a similar concentration to the protein samples tested.
- Clean and completely dry glass plates, combs, spacers (0.75-1 mm), and assemble the gel cassette.
- Electrophoresis. Performed at 100 V for approximately 2.5 h at 4 °C.
- Eliminating SDS from the gel. SDS in the gel may interfere with activity of the protease inhibitor to be tested, so it must be removed from gel before treating the gel with the protease. Removal is carried out by:
- Rinsing twice with 30 ml of 2.5% (v/v) Triton X-100 solution, for 10 min each with agitation.
- Rinsing twice with 30 ml of 2.5% (v/v) Triton X-100 + 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) solution, for 10 min each with agitation.
- Rinsing with 30 ml of 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), for 10 min with agitation.
- Rinsing twice with 30 ml of 2.5% (v/v) Triton X-100 solution, for 10 min each with agitation.
- For protein digestion, incubate the gel for 2 h at 37 °C, in a buffer solution containing 1.4 U of subtilisin in 50 ml of 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 200 mM NaCl.
- For fixation, place the gel in a 10% methanol, 10% acetic acid solution with gentle shaking for 30 min. Discard the solution.
- Detection of proteolysis inhibitors. Stain the gel with Coomassie Brilliant Blue, by adding approximately 100 ml of stain solution and leaving it in an orbital shaker overnight. Discard the stain and rinse the gel with water until the background gel becomes clear, which indicates the efficient degradation of the copolymerized gelatin. The presence of stained bands indicates areas where gelatin was protected from degradation by the activity of a protease inhibitor (hence “protection bands”).
- Commonly a twin gel, lacking gelatin is run in parallel as a control.
- If an antibody for the tested protease inhibitor is available, the digested gel can be transferred and an immunoblot assay can be performed.
Recipes
- Separating gel buffer (8x)
3 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8) - Stacking gel buffer (4x)
0.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) - Gelatin-SDS-PAGE Separating gel
Add the following solutions (total volume: 5 ml)30% acrylamide/bisacrylamide 2.08 ml dH2O 1.72 ml Separating gel buffer (8x) 0.625 ml 20% SDS 25 μl 1% gelatin solution 0.5 ml 10% ammonium persulfate 25 μl TEMED (add it right before pouring the gel) 5 μl - Stacking gel (total volume: 2.5 ml)
30% acrylamide/bisacrylamide 0.5 ml dH2O 1.375 ml Stacking gel buffer (4x) 0.625 ml 20% (w/v) SDS 15 μl 10% ammonium persulfate 15 μl TEMED 5 μl - Sample loading buffer
0.12 M Tris
10% 2-mercaptoethanol
20% (v/v) glycerol
2 mg/ml Bromphenol blue - Laemmli Reservoir buffer
25 mM Tris base
0.192 M Glycine
0.1% (w/v) SDS
pH around 8.3
Should not require adjustment
Store at room temperature - Stain solution (4 L)
Dissolve Coomassie blue G250 in ethanol and add phosphoric acid. Dissolve the ammonium sulphate in water and add to the mix. Adjust final volume with water.Coomassie blue R250 3.2 g Ethanol 800 ml Phosphoric acid 64 ml Ammonium sulphate 320 g
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from Jimenez-Duran et al. (2013).
References
- Jimenez-Duran, K., McClure, B., Garcia-Campusano, F., Rodriguez-Sotres, R., Cisneros, J., Busot, G. and Cruz-Garcia, F. (2013). NaStEP: a proteinase inhibitor essential to self-incompatibility and a positive regulator of HT-B stability in Nicotiana alata pollen tubes. Plant Physiol 161(1): 97-107.
- Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259): 680-685.
- Lantz, M. S. and Ciborowski, P. (1994). Zymographic techniques for detection and characterization of microbial proteases. Methods Enzymol 235: 563-594.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Bernal, L., García-Campusano, F., Nájera, E. and Cruz-García, F. (2013). Reverse Zymmogram Analysis for the Detection of Protease Inhibitor Activity. Bio-protocol 3(16): e856. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.856.
- Jimenez-Duran, K., McClure, B., Garcia-Campusano, F., Rodriguez-Sotres, R., Cisneros, J., Busot, G. and Cruz-Garcia, F. (2013). NaStEP: a proteinase inhibitor essential to self-incompatibility and a positive regulator of HT-B stability in Nicotiana alata pollen tubes. Plant Physiol 161(1): 97-107.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein
Biochemistry > Protein > Electrophoresis
Biochemistry > Protein > Modification
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link